- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- May 20, 2025
DIAGNOSING FABRY DISEASE IN CLINICAL PRACTICE
_430x268.jpg)
Clinical Manifestations of FD
Classical FD (<3% enzyme activity)
%20(1).png)
2nd decade
%20(1).png)
Symptoms appear later.
%20(1).png)
Neuropathic pain, angiokeratomas, and/or cornea verticillata are absent in females.
%20(1).png)
Childhood and adolescence
%20(1).png)
Neuropathic pain
%20(1).png)
Hypohidrosis and hyperhidrosis
%20(1).png)
Febrile crisis
%20(1).png)
Eye involvement*
%20(1).png)
Hearing loss
%20(1).png)
Angiokeratoma
%20(1).png)
Microalbuminuria
%20(1).png)
GI symptoms
%20(1).png)
2nd decade
.png)
Cardiomyopathy
.png)
Stroke and TIA
.png)
Macroproteinuria and eGFR loss
%20(1).png)
From 3rd decade
.png)
Progressive organ damage
.png)
Organ failure
.png)
Premature death
.png)
Nonclassical or late-onset FD (3%–30% enzyme activity) |
| Variable disease course and single organ involvement |
| Cardiac variant is common in late-onset FD |
| Identified in patients with stroke, renal failure, or cardiomyopathy |
| No neuropathic pain, angiokeratomas, and/or cornea verticillata |
.png)
FD diagnosis requires a multidisciplinary team approach involving:
| Biochemist |
| Pediatrician |
| Neurologist |
| Cardiologist |
| Dermatologist |
| Nephrologist |
| Geneticist |
.png)
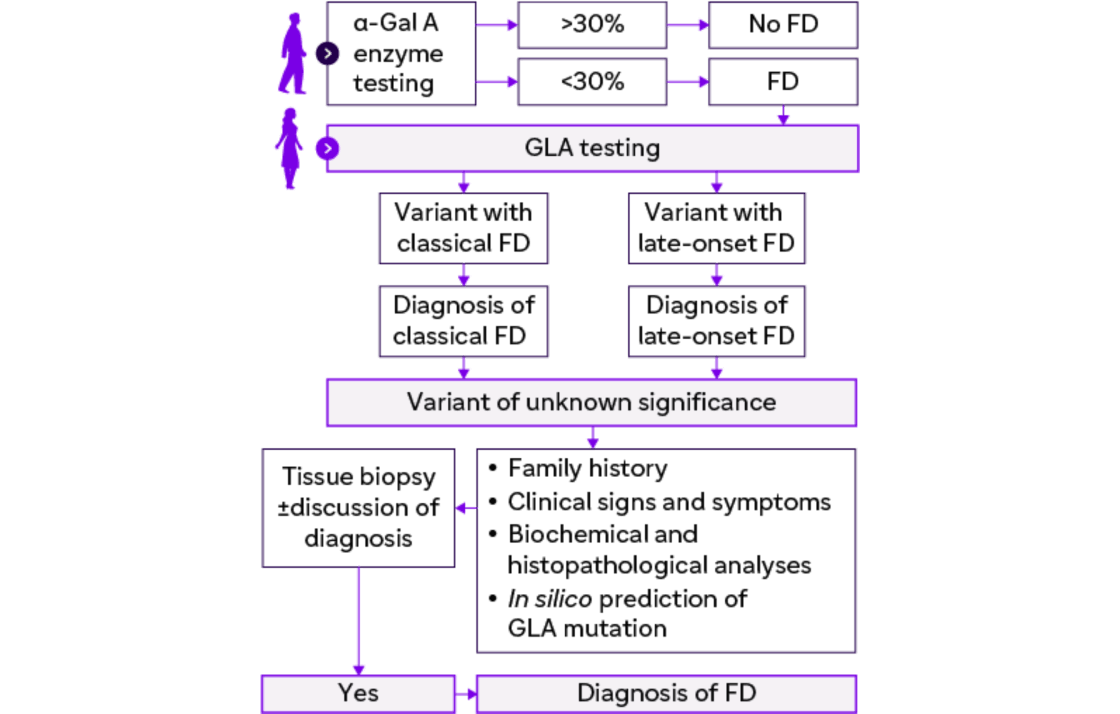
Suggested diagnostic algorithm for patient with clinically suspected FD
.png)
Testing for FD
1. Lyso-Gb3 indicates severity of FD
2. Endomyocardial and renal biopsies are used
3. Genetic testing
.png)
Testing for FD
- Causative mutation
- Affected family members
- Eligibility for treatment with migalastat
.png)
LSD referral centers to manage FD from diagnosis to long-term follow-up
.png)
FD:
|
Rare but underdiagnosed |
To be known and recognized by internal medicine physicians |
Early treatment can change the natural course of the disease. |
*Eye involvement includes cornea verticillata, tortuous retinal vessels, cataracts, and conjunctival lymphangiectasia.
Rare but To be known and recognized by underdiagnosed internal medicine physicians α-Gal A: Alpha-galactosidase; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate; GLA: α-Galactosidase A; FD: Fabry disease; GI: Gastrointestinal; LSD: Lysosomal storage disease; Lyso-Gb3: Globotriaosylsphingosine; TIA: Transient ischemic attack.
MAT-BH-2400131-V1-March 2024