- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- 18 Oct 2025
Head to Head Studies

Head-to-head studies Trurapi® vs NovoRapid®
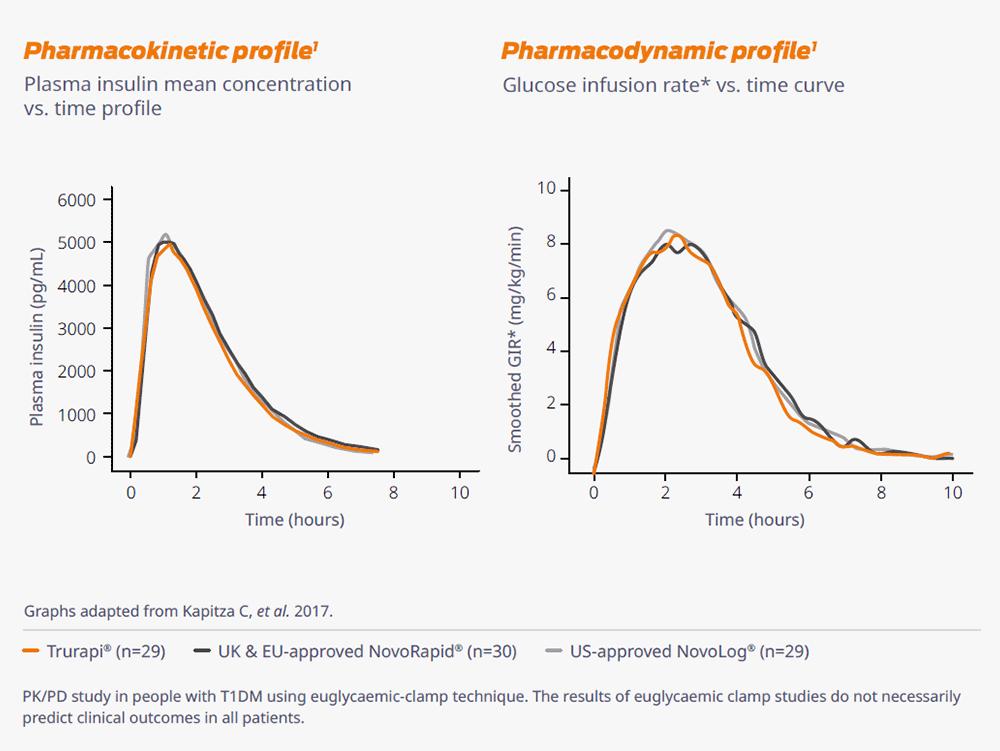.jpg)
Similar PK/PD profile in adults with T1DM1
PK/PD profiles in the biosimilar Trurapi®, were similar to the UK and EU-approved NovoRapid® and US-approved Novolog® in patients with T1DM.1
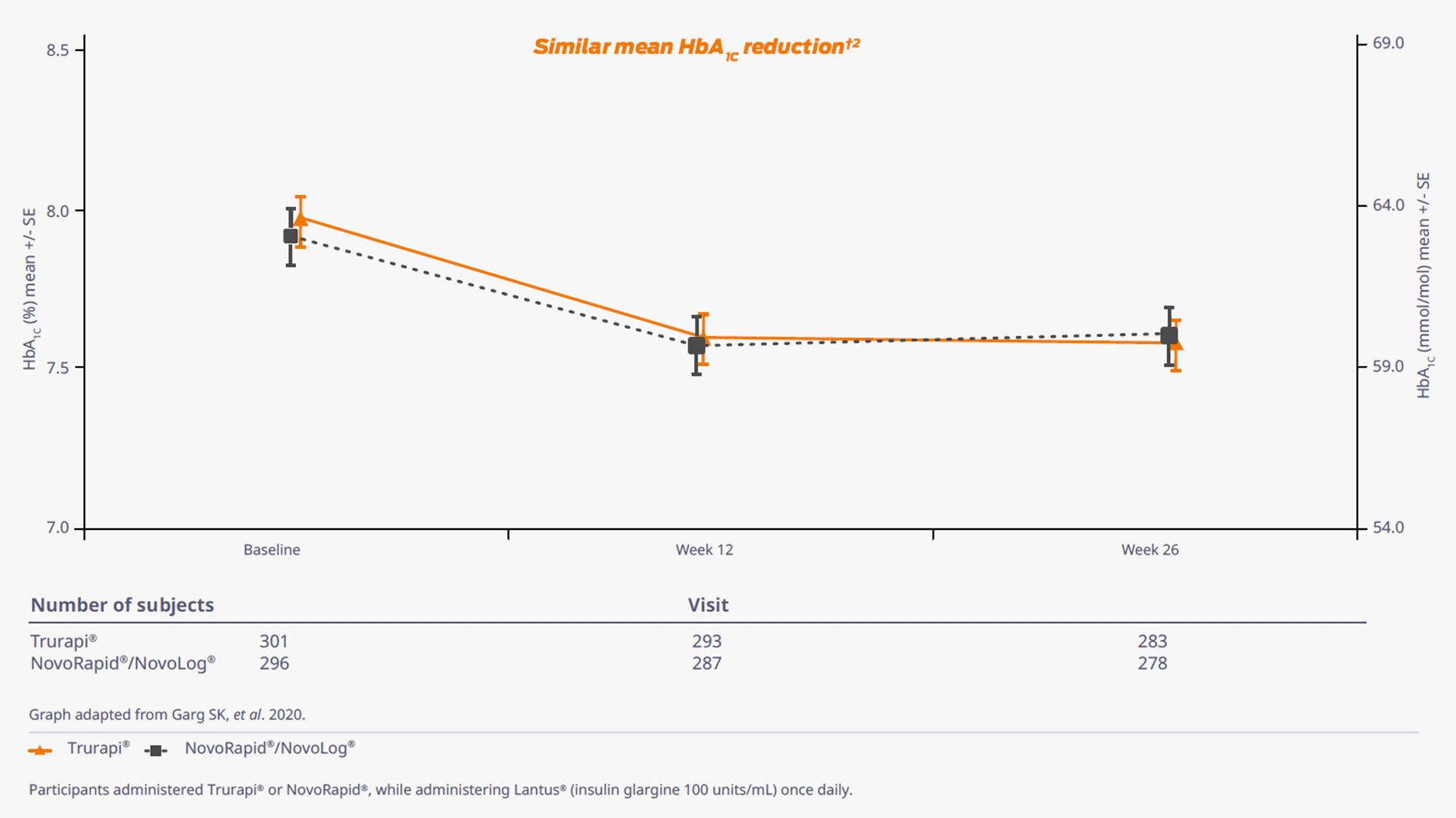
Similar mean HbA1C reduction in adults with T1DM and T2DM2
At week 26, HbA1C was -0.38% for Trurapi® group vs -0.30% for NovoRapid®/NovoLog® group. Similar mean HbA1C reduction from baseline to Week 26 in Trurapi® and NovoRapid®/Novolog® groups were observed in patients with either T1DM or T2DM.2
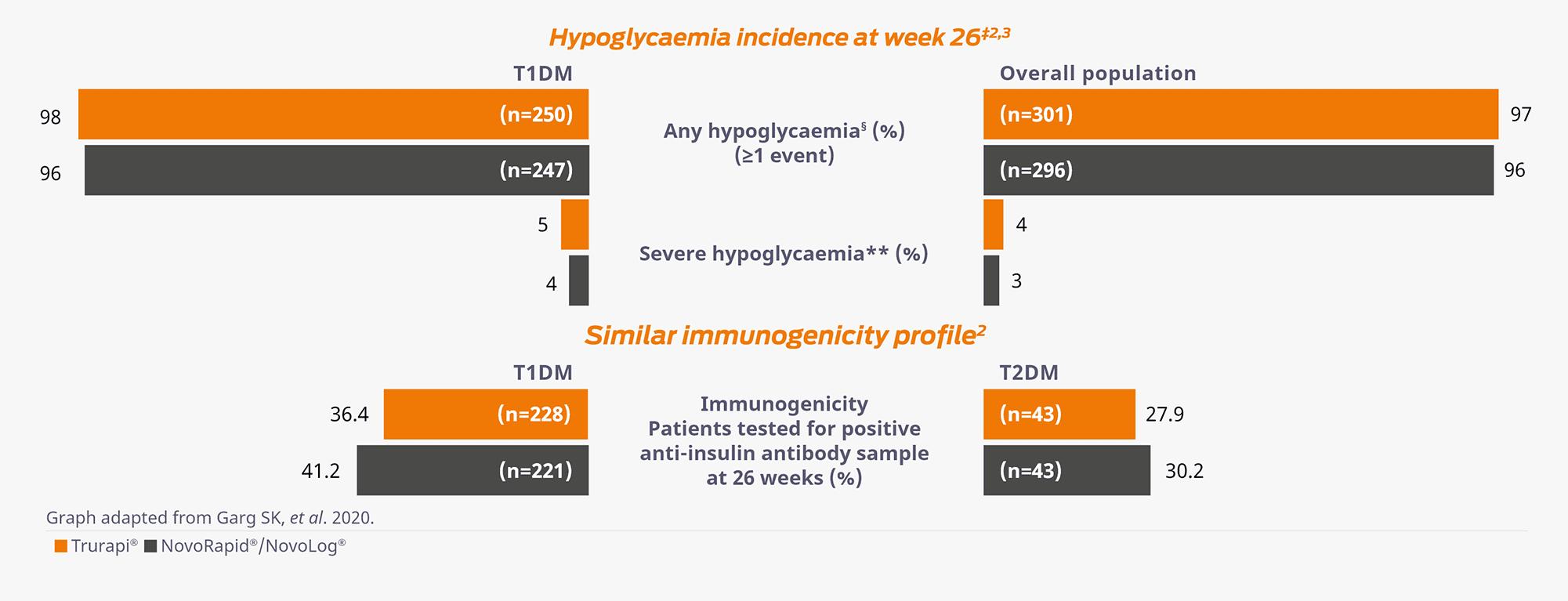
Similar long-term safety and tolerability profiles in adults with T1DM and T2DM2,3
Similar incidence rates of any hypoglycaemic events (≥1 event) in both the T1DM and overall population were observed in both Trurapi® and NovoRapid®/Novolog® groups.2,3
Want to know more about the bioequivalence data?
Watch this short video summarising the similar PK/PD profile (T1DM), efficacy, safety and tolerability profile (T1DM and T2DM) in Trurapi® vs. NovoRapid® from two clinical studies in adults.1,2
Abbreviations:
EU, European Union; HbA1C, glycated haemoglobin; PD, pharmacodynamic; PK, pharmacokinetic; SE, standard error; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; UK, United Kingdom.
*Mean smoothed body weight standardised glucose infustion rate. This was based on smoothed locally weighted regression in smoothed scattered (LOESS) plots; SAS, PROC LOESS, factor 0.06.1
†Endpoints were analysed in the intent-to-treat population.2
‡Hypoglycaemic data was derived from safety populations.2,3
§Any hypoglycaemia included documented symptomatic hypoglycaemia accompanied by a measured plasma glucose concentration of ≤70 mg/dL (≤3.9 mmol/L) and asymptomatic hypoglycaemia episodes (events not accompanied by typical symptoms of hypoglycaemia but with a measured plasma glucose concentration of ≤70 mg/dL [≤3.9 mmol/L]) were analysed separately and by using a lower more stringent plasma glucose concentration threshold of < 54 mg/dL (3.0 mmol/L).2
**Severe hypoglycaemia was an event requiring assistance of another person to actively administer carbohydrate, glucagon, or other resuscitative actions.2
Trurapi
Trurapi is indicated for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in adults, adolescents and children aged 1 year and above.

.png)

References
- Kapitza C, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(4):278–284.
- Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(2):85–95.
- Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(2):85–95. (Supplementary Figure S4).
MAT-XU-2300457 (v7.0) Date of Preparation: November 2025