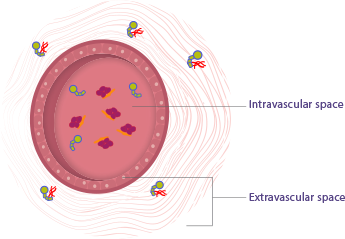
Factors VIII and IX follow different patterns of movement in the body1-4
- Endogenous factor IX distributes outside of the plasma and into areas such as the tissues, muscles, and joints, which is also called the extravascular space
- Factor VIII, however, is largely limited to the plasma, also called the intravascular space

Factor IX binds to type IV collagen,
which is located outside of the plasma5

Factor VIII binds to von Willebrand,
a protein located inside the plasma2-4
Type IV collagen binding may explain the activity of factor IX in the extravascular space and play a role in coagulation, as shown in preclinical data6
Additional research is needed to confirm these findings
This distinct behavior means that a single PK parameter alone may not reflect all of the factor IX activity in the body7,8
Preclinical data are not correlated with outcomes. Animal studies may not apply to humans. Additional research for preclinical data and research in humans is needed to confirm these findings.
PK=pharmacokinetic.

Explore Extravascular Distribution
Indication
References: 1. Chang P, Aronson DL, Borenstein DG, Kessler CM. Coagulant proteins and thrombin generation in synovial fluid: a model for extravascular coagulation. Am J Hematol. 1995;50:79-83. 2. Iorio A, Fischer K, Blanchette V, Rangarajan S, Young G, Morfini M. Tailoring treatment of haemophilia B: accounting for the distribution and clearance of standard and extended half-life FIX concentrates. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(6):1023-1030. 3. Lenting PJ, van Schooten CJM, Denis CV. Clearance mechanisms of von Willebrand factor and factor VIII. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(7):1353-1360. 4. Morfini M. The history of clotting factor concentrates pharmacokinetics. J Clin Med. 2017;6(3):35. 5. Iorio A, Fischer K, Blanchette V, et al. Tailoring treatment of haemophilia B: accounting for the distribution and clearance of standard and extended half-life FIX concentrates. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(6):1023-1030. 6. Gui T, Reheman A, Ni H, et al. Abnormal haemostasis in a knock-in mouse carrying a variant of factor IX with impaired binding to collagen type IV. J Thromb Haemost. 2009;7:1843-1851. 7. Feng D, Stafford KA, Broze GJ, Stafford DW. Evidence of clinically significant extravascular stores of factor IX. Thromb Haemost. 2013;11(12):2176-2178. 8. Stafford DW. Extravascular FIX and coagulation. Thrombosis J. 2016;14(suppl 1);35.