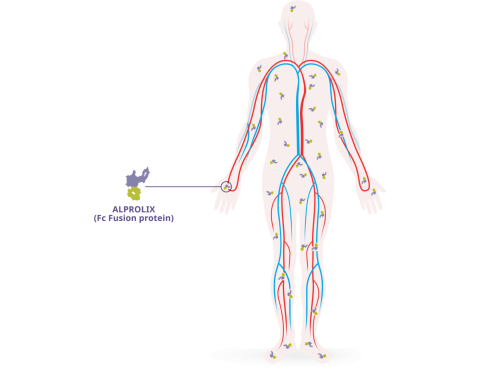
- VOD is a PK parameter that quantifies the movement of infused factor IX between the intravascular and extravascular spaces1
- ALPROLIX has a high* VOD–327 mL/kg for a 50 IU/kg dose†–which suggests that it travels to areas of the body outside the intravascular space, similar to endogenous factor IX2,3
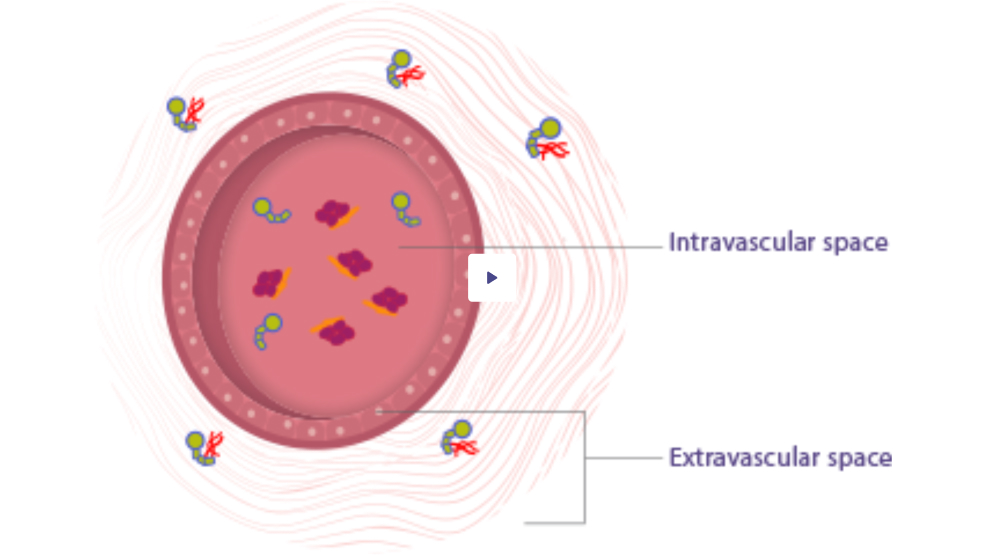
Additional research is needed to understand the clinical implications of VOD.
* Based on the theoretical plasma volume of 40 mL/kg in adults.4
† The subgroup receiving 100 IU/kg of ALPROLIX has a reported VOD of 236 mL/kg. The difference in reported values is within normal variation and may be due to intersubject variability. This assessment is based on the adult population; a high VOD has also been observed for children and adolescents at the 50 IU/kg and 100 IU/kg doses.2,8
Fc Fusion technology is thought to be related to the extravascular distribution of ALPROLIX2-4
- The extravascular distribution of ALPROLIX, as well as its clearance from the body–3.3 mL/h/kg for a 50 IU/kg dose in adults–help to extend its half-life2,5
- ALPROLIX also degrades naturally into amino acids and does not accumulate in the body6
This PK profile indicates that trough does not measure all of the ALPROLIX in the body.
The ISTH recommends that multiple PK parameters should be evaluated, including half-life, VOD, and clearance1-3,7
See why ALPROLIX is a flexible factor IX product for all dosing scenarios2
INDICATION:
ISTH=International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis; PK=pharmacokinetic; VOD=volume of distribution.
References: 1. McNamara PJ, Leggas M. Drug distribution. In: Hacker M, Messer W, Bachmann K, eds. Pharmacology: Principles and Practice. Burlington, MA: Elsevier Academic Press; 2009:113-127. 2. ALPROLIX [package insert]. Waltham, MA: Bioverativ Therapeutics Inc. 3. Diao L, Li S, Ludden T, Gobburu J, Nestorov I, Jiang H. Population pharmacokinetic modelling of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc) in patients with haemophilia B. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2014;53(5):467-477. 4. Iorio A, Fischer K, Blanchette V, Rangarajan S, Young G, Morfini M. Tailoring treatment of haemophilia B: accounting for the distribution and clearance of standard and extended half-life FIX concentrates. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(6):1023-1030. 5. Björkman S. Comparative pharmacokinetics of factor VIII and recombinant factor IX: for which coagulation factors should half-life change with age? Haemophilia. 2013;19:882-886. 6. Shapiro A. Development of long-acting recombinant FVIII and FIX Fc fusion proteins for the management of hemophilia. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2013;13(9):1287-1297. 7. Ragni MV, Croteau SE, Morfini M, et al. Pharmacokinetics and the transition to extended half-life factor concentrates: communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16(7):1437-1441. 8. Björkman S. Population pharmacokinetics of recombinant factor IX: implications for dose tailoring. Haemophilia. 2013;19(5):753-757.