- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- Sep 16, 2025
Mechanism of Smoldering Disease

Smoldering neuroinflammation is driven primarily by disease-associated microglia found in the CNS and contributes to both physical and cognitive disability accumulation1-3
- Microglia are key orchestrators of smoldering neuroinflammation in the CNS, resulting in disability accumulation1,4
- Even in the earliest stages of MS, microglia shift from a homeostatic to a disease-associated state1
Innate immunity predominantly drives smoldering neuroinflammation1
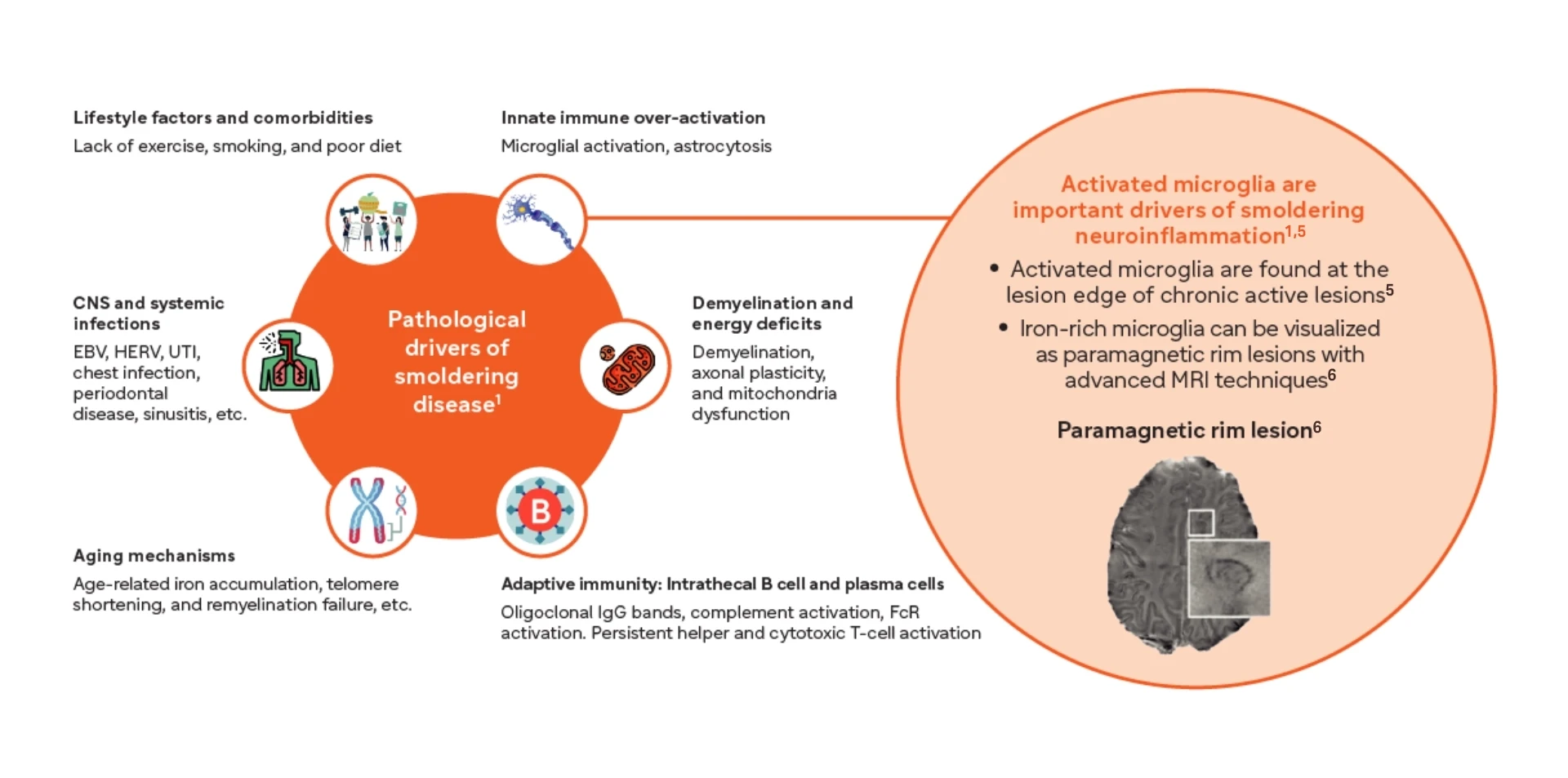
From peripheral triggers to central drivers: the evolving pathophysiology of acute and smoldering neuroinflammation7,8
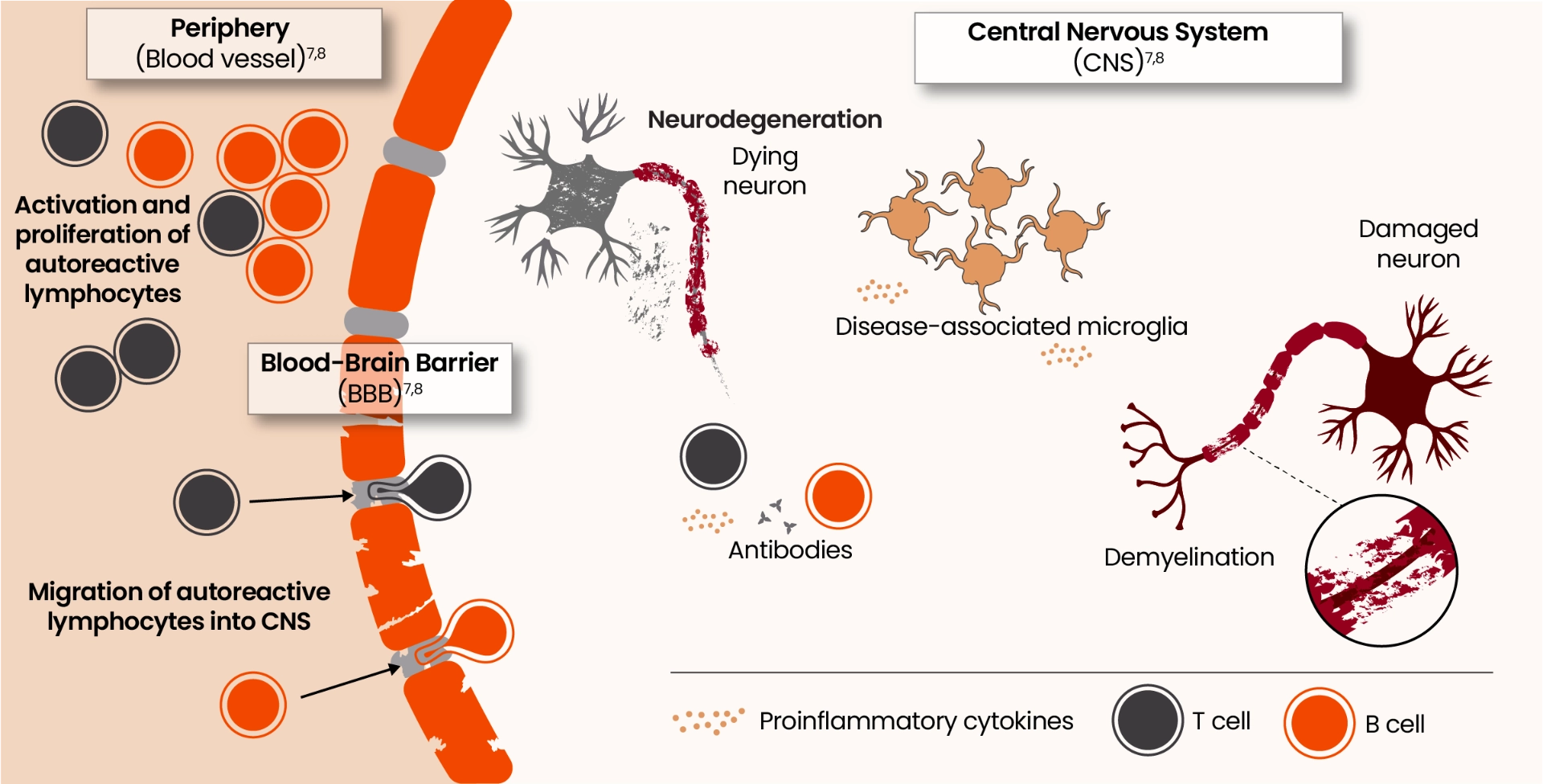
Microglia are key orchestrators of smoldering neuroinflammation in the CNS resulting in disability accumulation9
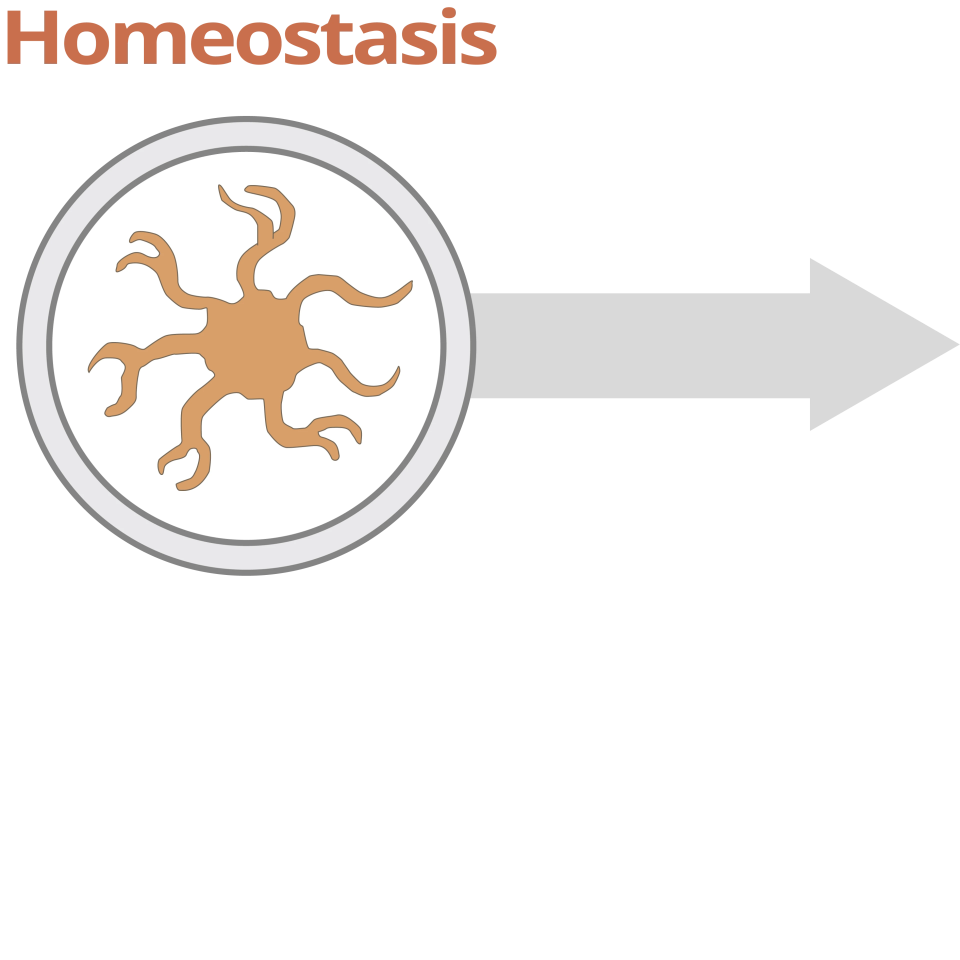
Homeostatic microglia play an important role in regulating myelimation and remyelination, synaptic maintenance, blood-brain barrier permeability, and neurogenesis.10

Even in the earliest stages of MS, microglia shift from a homeostatic to a disease-associated state. 11,12
- Microglia-driven smoldering nouroinflammation begins even before the first clinically apparent relapse or acute lession 1,13,14,15
- Iron-laden microglia surround the lesion edge of paramagnetic rim lesions and are associated with increased disability in both RRMS and SPMS16-17
- Microglia are upregulated in SPMS and are thought to play a significant role in driving disability accumulaton16-18
- Microglia-induced synaptic loss has been associated with cognitive loss19-21

Microglia are upregulated in SPMS and are thought to play a significant role in driving disability accumulation.17,22

Iron-laden microglia surround the lesion edge of paramagnetic rim lesions* (PRLs) and are associated with increased disability in both RRMS and SPMS.23
Microglia-induced synaptic loss has been associated with cognitive loss.19-21
For more information about Acute and Smoldering Inflammation, click on this link:
*PRLs are a type of chronic active lesion (CAL).
CNS, central nervous system; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; HERV, human endogenous retroviruses; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; MS, multiple sclerosis; UTI, urinary tract infection.
- Giovannoni G, Popescu V, Wuerfel J, et al. Smouldering multiple sclerosis: the ‘real MS’. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2022;15:17562864211066751. doi:10.1177/17562864211066751
- Häusser-Kinzel S, Weber MS. The role of B cells and antibodies in multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, and related disorders. Front Immunol. 2019;10:201. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00201
- Frisch ES, Pretzsch R, Weber MS. A milestone in multiple sclerosis therapy: monoclonal antibodies against CD20—yet progress continues. Neurotherapeutics. 2021;18(3):1602-1622.
- Correale J. The role of microglia activation in disease progression. Mult Scler J. 2014;20(10):1288-1295
- Absinta M, et al. J Clin Invest 2016;126(7):2597-2609
- Abstina M, et al. Nature 2021; 597(7878):709-714
- Gandhi R, Laroni A, Weiner HL. Role of the innate immune system in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2010;221(1-2):7-14.
- Reich DS, Lucchinetti CF, Calabresi PA. Multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(2):169-180.
- Hermandez-Pedro NY, Espinosa-Ramirez G, de la Cruz VP, Pineda B, Sotelo J. Initial immunopathogenesis of multiple sclerosis:innate immune response. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:413413465.doi:10.1155/2013/413465
- Sierra A, Paolicelli RC, Kettenmann H. Cie nanos de microglia: milestones in a century of microglia research. Trends Neurosci.2019;42(11):778-792
- Zzravy T et al. Loss of ‘homeostatic’ microglia and patterns of their activation in active multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2017;140:1900-1913
- O’Loughlin E, Madore C, Lassmann H, Butovsky O. Microglial phenotypes and functions in multiple sclerosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(2):a028993.doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a028993
- 1Giovanni G. The neurodegenerative prodome in multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol. 2017;16(6):413-414
- Giannetti P, Politis M, Su P et al. Increased PK11195-PET binding in normal-appearing white matter in clinically isolated syndrome. Brain, 2015;138(1):110-119
- Cortese M, Riise T et al. Preclinical disease activity in multiple sclerosis: A prospective study of cognitive performance prior to first symptom. Ann Neurol. 2016;80(4):616-624
- Abstina M, Lassmann H et al. Mechanisms underlying progression in multiple sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2020;33(3):277-285
- Kamma E, Lasisi W, Libner C, Ng HS, Plemel JR. Central nervous system macrophages in progressive multiple sclerosis: relationship to neurodegeneration and therapeutics. J Neuroinflammation. 2022;19(1):45. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02408-y
- Gruber RC, Dufault MR, et al. Establishing a role for the Bruton’s Turosine Kinase Inhibitor Tolebrutinib in modulating neuroinflammation and disease progression in MS. Presented at: American Academy of Neurology: April 17-22, 2021; San Francisco, CA, Platform S25:00
- Friese MA. Widespread synaptic loss in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2016;139(pt 1):2-4.
- Jürgens T, Jafari M, Kreutzfeldt M, et al. Reconstruction of single cortical projection neurons reveals primary spine loss in multiple sclerosis. Brain. 2016;139(pt 1):39-46.
- Werneburg S, Jung J, Kunjamma RB, et al. Targeted complement inhibition at synapses prevents microglial synaptic engulfment and synapse loss in demyelinating disease. Immunity. 2020;52(1):167-182.
- Gruber RC, Chretien N, Dufault MR, et al. Central effects of BTK inhibition in neuroinflammation. Presented at: AAN Annual Meeting; April 25-May 1, 2020; Toronto, Canada.
- Absinta M, Sati P, Masuzzo F, et al. Association of chronic active multiple sclerosis lesions with disability in vivo. JAMA Neurol. 2019;76(12):1474-1483.
MAT-KW-2500337/v1/Sept2025