- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- Jul 21, 2025
Considerations for bullous pemphigoid management
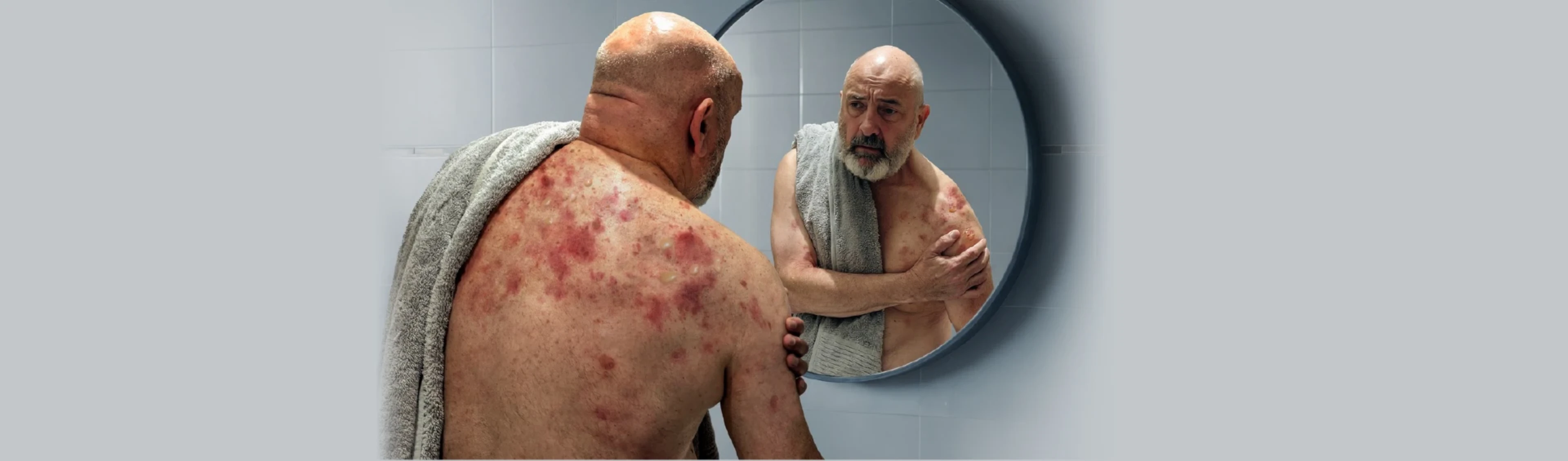
Bullous pemphigoid management: The complexities of treating a chronic skin disease in a fragile patient population
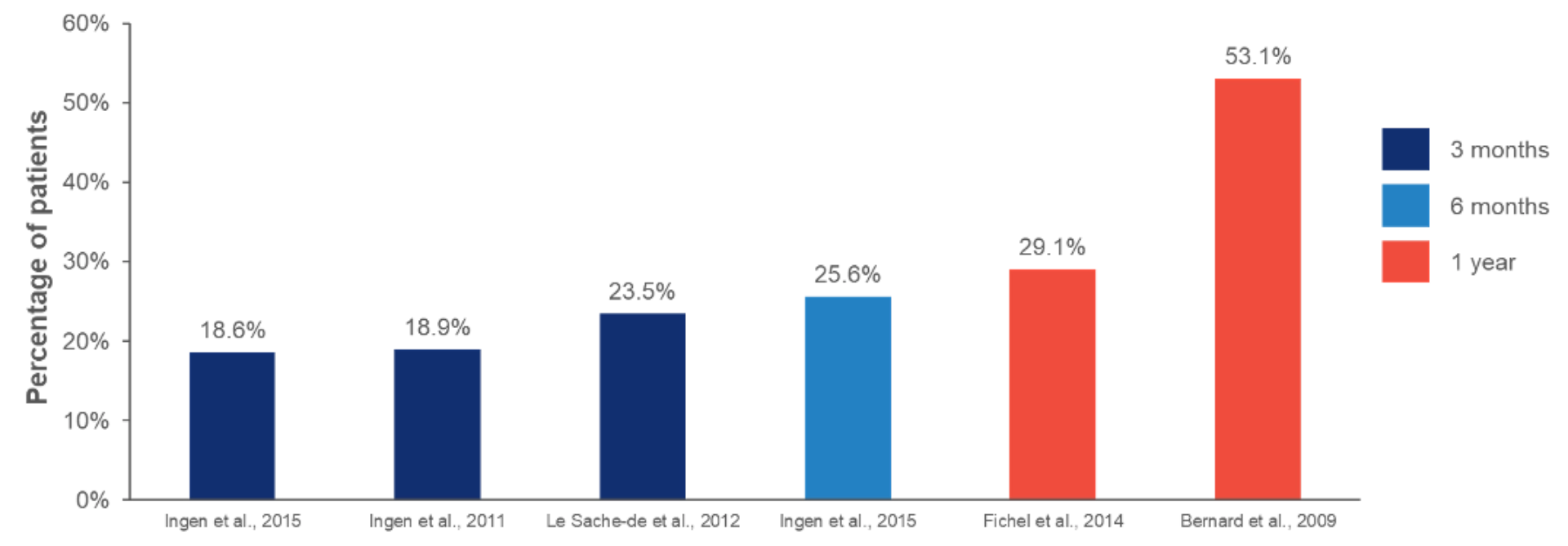
Bullous pemphigoid can have relapse rates of up to 53%, regardless of treatments1,2
.png)
The relapse rate of bullous pemphigoid is high – up to 53%, and the majority of relapses occur within 6 months of remission1
Estimated relapse rates of patients with bullous pemphigoid at different timepoints after disease remission or treatment withdrawal, based on a meta-analysis study1
.webp)
Figure adapted from Wang Y, et al. Ann Med. 2018.
The ultimate goal of bullous pemphigoid management is long-term disease control3
Treatment for bullous pemphigoid should aim to:3–7

.webp)
.webp)
.webp)
Treatment strategies should account for the distinct challenges of bullous pemphigoid8–12
As bullous pemphigoid is most prevalent in the elderly, treatment strategies should consider the following key challenges of older patients with bullous pemphigoid8–12
.png)
High burden of bullous pemphigoid itself, and comorbidities9,11
.png)
Increased risk of adverse events with corticosteroids and other immunosuppressants
8,9,13
Risks associated with polypharmacy12

Age-related changes in drug metabolism and decreased drug tolerance10
Due to the chronicity of bullous pemphigoid, a safe and effective long-tern management approach is needed to reduce the risk of relapse and achieve disease remission11
-
Wang Y, et al. Ann Med. 2018;50(3):234–9.
-
Fincel, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2014;150(1):25–33.
-
Borradori L, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022;36(10):1689–04.
-
Lee J, et al. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2219.
-
Hopkins ZH, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2023;159(11):1185–94.
-
Chang TH, et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2023;103:adv5329.
-
Tedbirt B, et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157(4):421–30.
-
Pratasava V, et al. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(10):1061.
-
Khalid SN, et al. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021;70:102799.
-
Kinirons MT and O’Mahony MS. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;57(5):540–4.
-
Bernard P and Antonicelli F. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2017;18(4):513–28.
-
Försti AK, et al. Acta Derm Venereol. 2016;96(6):758–61.
-
Meurer M. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30(1):78–83.
MAT-SA-2500498/V2/June 2025