- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- 15 May 2025
Real-world evidence
The results from real world data analyses are limited by potential selection bias, as treatment groups often show differences in baseline characteristics. Outcome definitions may differ between RCTs and RWD analyses, and clinical events cannot be adjudicated. Certain clinical parameters may not be present in observational data; these analyses are subject to limitations.
NIRSE-GAL, Spain1
Nirse-GAL study (Galicia, Spain) measured the effectiveness in preventing hospitalisation and public health impact of Beyfortus in infants born during and before RSV season1a
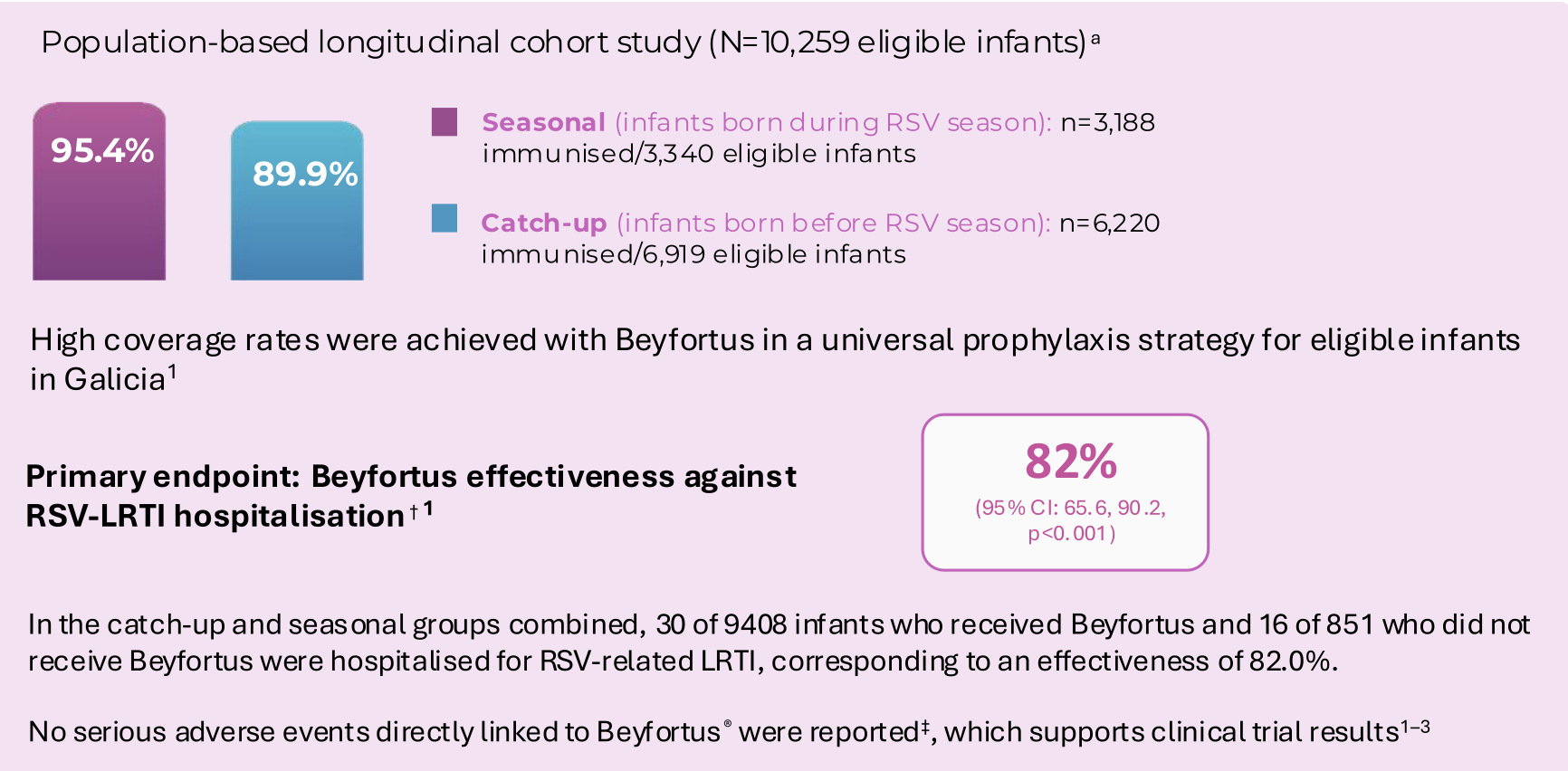
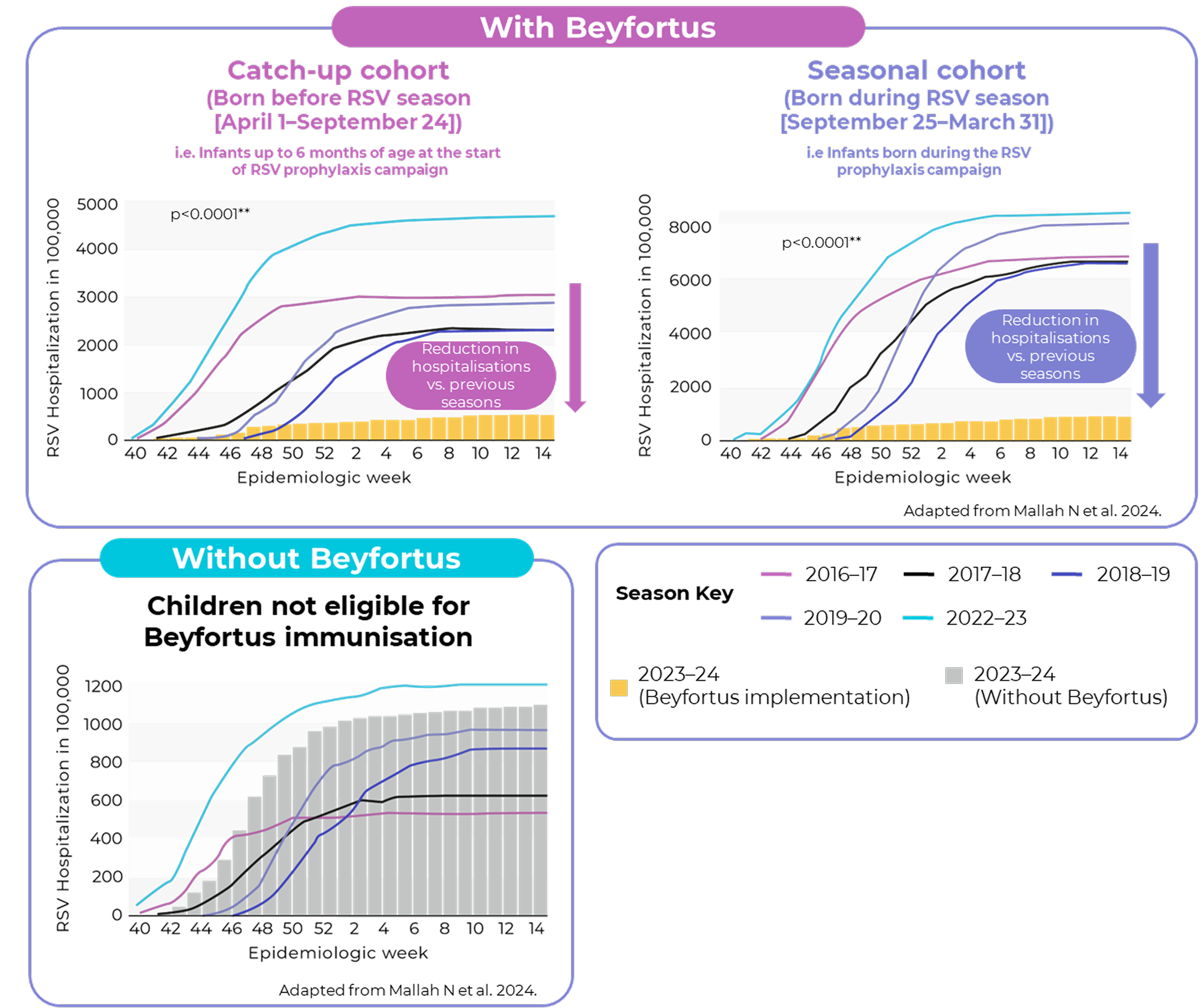
Public health impact of Beyfortus on RSV hospitalisation in Galicia, Spain
After Beyfortus implementation, RSV LRTI hospitalisation decreased by 89.2%* vs. five previous seasons for infants in the overall cohort (infants born before and during RSV season)†2
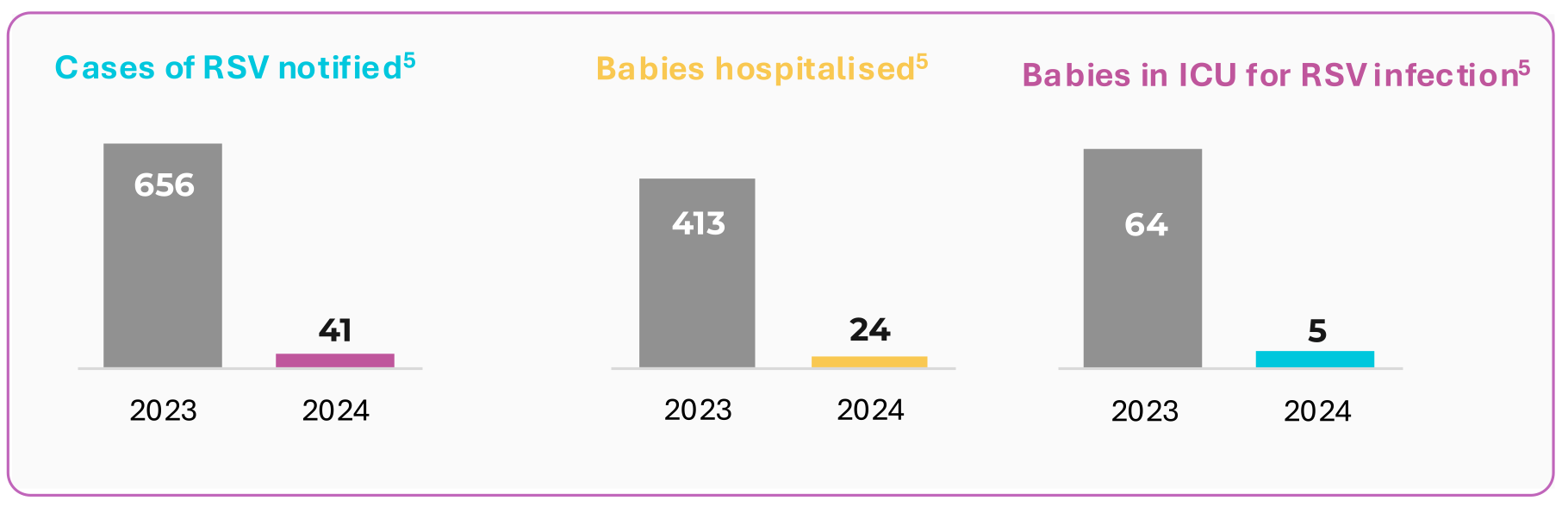
Ireland new HSE RSV immunisation programme5
Beyfortus significantly reduced infections, serious illness and hospitalisations amongst babies born in Ireland since 1st September 2024 compared to the same period in the previous year.

AE, adverse event; GA, gestational age; LRTI, lower respiratory tract disease; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus.
a. Immunisation campaign: September 25, 2023–March 31, 2024. Eligible infants in Galicia included those aged <6 months at the start of the immunisation campaign (born between April 1 and September 24, 2023 [catch-up group]) and those born during the immunisation campaign (born between September 25 2023 and March 31 2024 [seasonal group]. A high-risk group was also immunised (n=348/360) as part of the Galician immunisation campaign. This group was not included in effectiveness or public health impact calculations.1
† Effectiveness and impact were estimated using the seasonal and catch-up groups. Nirsevimab effectiveness was estimated from incidence rate ratios calculated using Poisson regression models, which were adjusted for enrolment group (catch-up and seasonal), sex, and health district area. Only patients with non-zero follow-up time were included.1
‡ Adverse events related to Beyfortus administration were routinely monitored through the Galician pharmacovigilance system. In addition, active surveillance of any potential adverse event or hospitalisation in the first 3 weeks after Beyfortus administration was conducted in the pre-term population (infants with a GA <37 weeks).2
* IQR: 89.1–91.4%. **P-values were obtained from linear regression model analysis of weekly accumulated incidence rates comparing the 2023–2024.
- Ares-Gómez S et al. Lancet Infect Dis 2024; 24(8): 817–824.
- Mallah N et al. Lancet Infect Dis 2024; 25(2): E62–E63 & Supplementary Appendix.
- Griffin MP et al. N Engl J Med 2020; 383(5): 415–425.
- Hammitt LL et al. N Engl J Med 2022; 386(9): 837–846.
- HSE press release. Available at https://about.hse.ie/news/new-hse-rsv-immunisation-programme-significantly-reduces-infections-serious-illness-and-hospitalisations-in-babies/. Last accessed May 2025.
MAT-XU-2501637 (v2.0) Date of preparation: September 2025
