The safety of Qfitlia has been extensively studied in the largest hemophilia preapproval clinical program1,2
| Adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients treated with the AT-DR of Qfitlia (N=286)1 | |
|---|---|
| Adverse reaction | % of patients |
| Viral infection* | 29 |
| Nasopharyngitis* | 26 |
| Bacterial infection* | 11 |
| Hepatic injury† | 8 |
| Arthralgia* | 8 |
| Prothrombin fragment 1.2 increased | 7 |
| Injection site reaction‡ | 6 |
| Headache | 5 |
| Cough* | 5 |
* Includes similar terms.1
† Hepatic injury includes increased ALT, increased AST, and liver injury.1
‡ Includes injection site bruising, injection site erythema, injection site pain, injection site hematoma, injection site atrophy, injection site hemorrhage, injection site discomfort, injection site swelling, injection site discoloration, injection site pruritus, injection site induration, injection site nodule, injection site mass, injection site vesicles, injection site deformation, injection site rash, injection site joint pain, and application site erythema.1
Heptotoxicity1
• On the AT-DR, 3.4% of patients treated with Qfitlia had at least one ALT value greater than 3x ULN, with a median onset of 89 days after initial dosing (range: 15 to 768 days)1
• Dosage interruptions due to increased transaminases occurred in 2/286 (0.7%) patients1
• Avoid use of Qfitlia in patients with established hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, and C)1
• Obtain baseline LFTs, including AST, ALT, and total bilirubin, prior to initiating Qfitlia; monthly for at least the first 6 months of Qfitlia use; monthly for at least 6 months after a dose increase; and periodically thereafter as clinically indicated1
Low discontinuation rates due to adverse events were observed in 1.4% (4/286) of patients1
• Adverse reactions that resulted in permanent discontinuation of Qfitlia included liver injury, postoperative deep vein thrombosis, cerebral infarction, and pruritus1
AT-DR mitigates the risk of thrombotic events (TEs)1
The risk of thrombosis is greater in patients with1:
• Persistent antithrombin activity <15%
• Presence of comorbidities that predispose a patient to thrombosis
• Nonadherence to Bleed Management Guidelines (BMG) in the postoperative state
• Presence of indwelling venous catheters
• Use of Qfitlia at a fixed dose of 80 mg monthly (non–antithrombin-based dosing)
Fixed monthly dose of 80 mg
TEs were reported in 2.6% of patients receiving a fixed monthly dose of Qfitlia 80 mg, including a fatal event of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. The fixed 80 mg once monthly dose is not approved or recommended for use.1
AT-DR
An antithrombin-based dosing regimen (AT-DR) was implemented to mitigate TE risk1
- 1.4% of patients receiving Qfitlia prophylaxis under the AT-DR experienced TEs1
| Patients who experienced TEs under the AT-DR had multiple risk factors2 | ||||
| Patient details |
Patient A |
Patient B |
Patient C |
Patient D |
| Nonadherence to the BMG | - | - | aPCC dosing exceeding BMG | FVIII dosing exceeding BMG for over 14 days |
| Clinical risk factors |
• Diabetes |
• Diabetes |
• Extended PIV line |
• Hypertension |
How to mitigate TE risk1
• Monitor antithrombin levels using an FDA-cleared test and target antithrombin activity in the range of 15% to 35%1
• Patients treated with Qfitlia should follow the Bleed Management Guidelines and be monitored for signs or symptoms of thrombotic events1
• If breakthrough bleeding occurs after 7 days from the first dose of Qfitlia, bleeds should be managed with a reduced dose and frequency of factor/BPA to minimize the risk of thrombotic events1
Gallbladder events reported in the ATLAS clinical trial program1
Treatment with Qfitlia is associated with an increased occurrence of acute and recurrent gallbladder disease, including cholelithiasis and cholecystitis. The fixed 80 mg monthly dosing is not approved or recommended for use.1
Gallbladder events in the trial program1
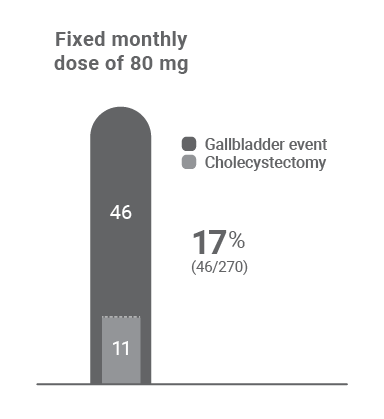
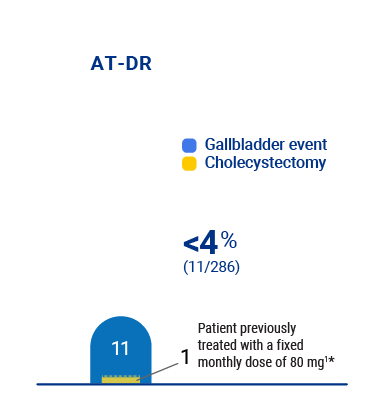
• All but one patient resumed treatment after cholecystectomy surgery1
• One patient who started on fixed dosing experienced cholangitis and pancreatitis caused by gallstone disease more than a year after cholecystectomy, while on the AT-DR1
* Cholecystectomy occurred while patient was on the AT-DR.1
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of acute and recurrent gallbladder disease1
• Patients diagnosed with acute or recurrent gallbladder disease in the clinical program most commonly presented with epigastric pain, generalized abdominal pain, indigestion, nausea, and/or vomiting1
• Interrupt or discontinue Qfitlia if acute or recurrent gallbladder disease occurs1
• Consider alternative treatment for patients with a history of symptomatic gallbladder disease1
INDICATION
ALT=alanine aminotransferase; AST=aspartate aminotransferase; AT-DR=antithrombin-based dosing regimen; aPCC=activated prothrombin complex concentrate; BPA=bypassing agent; FDA=US Food and Drug Administration; FVIII=Factor VIII; LFTs=liver function tests; PIV=peripheral intravenous catheter; PwH=people with hemophilia; ULN=upper limit of normal.
References: 1. Qfitlia Prescribing Information. Genzyme Corporation. Cambridge, MA. 2. Young G, et al; for the ATLAS-OLE Trial Group. Safety and efficacy of the fitusiran revised antithrombin-based dose regimen (AT-DR) in people with haemophilia (PwH) A or B, with or without inhibitors (ATLAS-OLE). Presented at: European Association for Haemophilia and Allied Disorders Annual Congress; February 6-9, 2024; Frankfurt, Germany.

