- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- 17 Sep 2025
AD Disease Overview
Disease Overview
Atopic dermatitis (AD), is a common chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin that can flare periodically throughout life. It most often begins in childhood but can affect individuals of any age.1-3
Diagnostic Criteria for Atopic Dermatitis (AD)
Atopic dermatitis is diagnosed clinically, based on a combination of essential, important, and supportive features, as well as by excluding
other similar skin conditions. There is no single definitive laboratory test for AD4-6.

Essential Features (Must Be Present)
Pruritus (itching): Persistent itching is the hallmark of 4,5
Eczema: This includes acute, subacute, or chronic skin changes such as erythema and scaling, with a typical age-specific distribution (e.g., cheeks and extensor surfaces in infants; flexural areas in older children and adults) 4,5
Chronic or Relapsing Course: Symptoms must have a history of chronicity or recurring flares4,5

Important Features (Support Diagnosis)
- Personal or Family History of Atopy: Includes atopic diseases such as asthma, allergic rhinitis, or food allergies4,5,7
- Early Age at Onset: Most cases begin in childhood, often before age five4,5
- Immunoglobulin E (IgE) Reactivity: Elevated IgE levels are common but not required4
- Xerosis: Dry skin is frequently observed4,5

Associated Features (Suggestive but Nonspecific)
- Atypical Vascular Responses: Such as facial pallor or white dermographism.5
- Skin Findings: Keratosis pilaris, pityriasis alba, hyperlinear palms, ichthyosis, lichenification, prurigo lesions.5
- Ocular or Periorbital Changes: Such as Dennie-Morgan folds.5
Exclusionary Conditions
- Diagnosis also requires exclusion of other conditions that can mimic AD, including:
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Contact dermatitis
- Scabies
- Tinea (fungal) infections
- Immunodeficiency syndromes
- Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
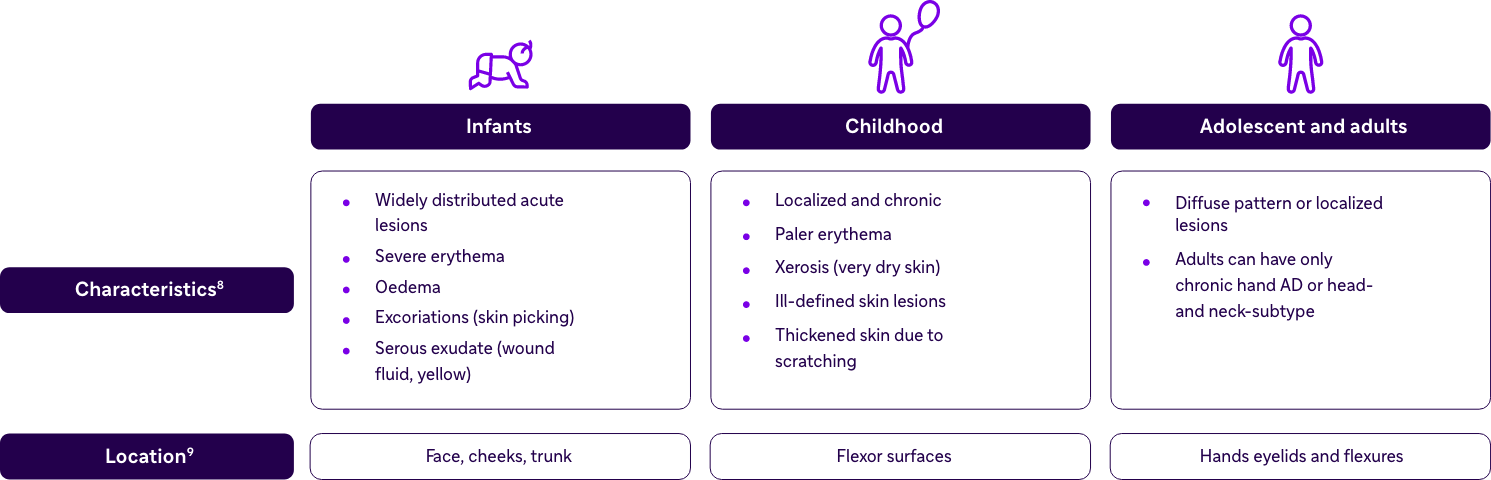
Clinical Features of Patients With AD
- Clinical diagnosis can be difficult in infants, toddlers and in elderly people8
- Skin biopsies in adults help exclude malignant diseases (e.g. cutaneous T cell lymphoma)8
- AD lesions typically show an age-related distrubution8,9
1. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24299-atopic-dermatitis
2. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atopic-dermatitis-eczema/symptoms-causes/syc-20353273
3. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/atopic-dermatitis
4. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2020/0515/p590.html
5. https://anndermatol.org/DOIx.php?id=10.5021%2Fad.24.049
6. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/guidelines-for-the-diagnosis-and-assessment-of-eczema
7. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/atopic-dermatitis/diagnosis-treatment-and-steps-to-take
8. Weidinger S, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4(1):1
9. Avena-Woods C. Am J Manag Care. 2017;23(8 Suppl):S115-S123.
MAT-KW-250016-V1.0-04/2025