- Article
- Source: Campus Sanofi
- 7 Nov 2025
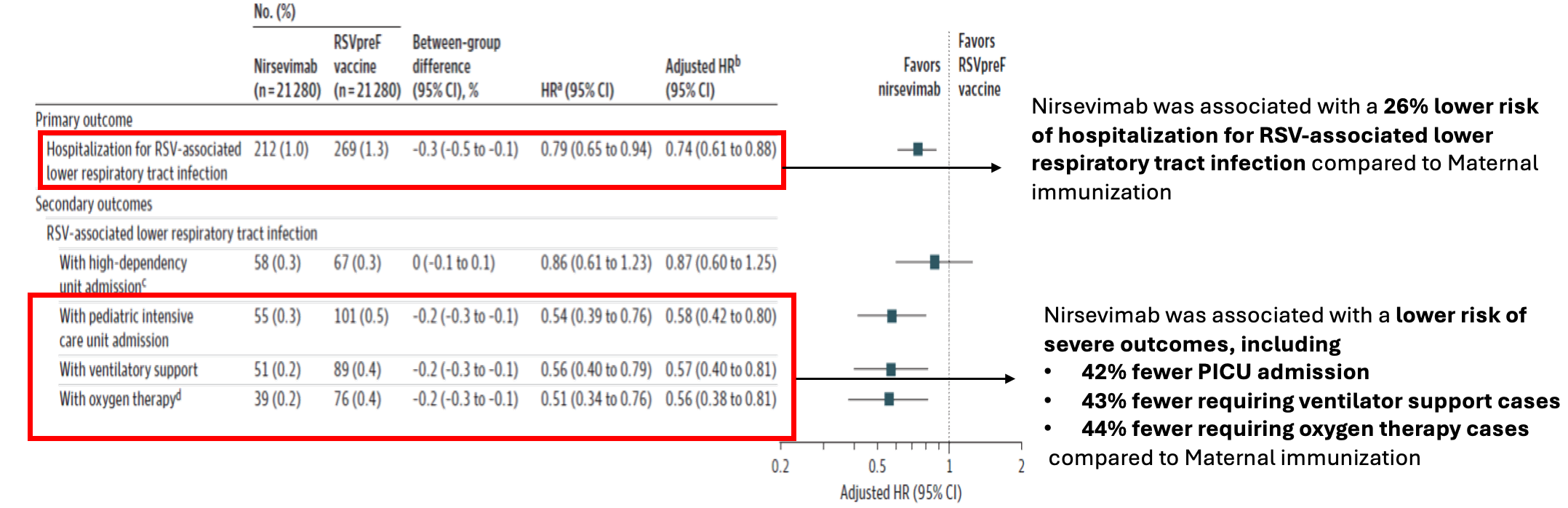
RWE data on Nirsevimab and RSV preF vaccine
First head-to-head comparison of Nirsevimab vs RSVpreF Vaccine for RSV Related Hospitalization in Newborns in France
Published on: 22nd DECEMBER 2025
Research design and methods:
- Population based cohort study
Study Population:
- A total of 42,560 infants were included in the study
Comparison of the public health impact of RSV disease prevention options for infants:
a static decision model of the US birth cohort
Published on: 25 November 2025
Research design and methods:
- Using a static decision-analytic model estimated the public health impact in terms of RSV-related outcomes and costs in a US birth cohort during their first RSV season compared to the pre-2023 SoP of:
Long-acting mAb
It is indicated for prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
lower respiratory tract disease in neonates and infants during their first RSV season.
Maternal vaccination
RSVpreF is a bivalent prefusion-stabilized viral surface protein vaccine4
Licensed for use in pregnancy for passive immunization
of infants4
Results:
| Nirsevimab | Nirsevimab | |
| MA RSV health events | 364,204 | 76,915 |
| RSV related hospitalization | 32,404 | 9,649 |
| Emergency room visits | 88,647 | 17,228 |
| Primary care visits | 243,10 | 50,029 |
| Primary care visits | $1.29 billion | $345 million |
Conclusion:
“All options are expected to reduce the impact of RSV disease, but giving Nirsevimab to all infants was predicted to prevent the most illnesses, hospitalizations, and costs.”
Results:
Number need to immunize to:
|
|
Avert one RS case |
Avert one* hospitalization |
Avert one ICU |
Avert one MV |
Avert one ER visit |
Avert one primary care visit |
Avert one death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
nirsevimab - all infants |
9 |
91 |
324 |
1,365 |
34 |
13 |
58,668 |
|
RSVpref - preterm&term - infants† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Seasonal |
19 |
149 |
498 |
1,867 |
84 |
29 |
141,639 |
|
Year-round |
23 |
222 |
785 |
3,233 |
96 |
35 |
174,159 |
*Hospitalization here includes cases that resulted in an ICU admission or MV case.
†Results provided for preterm and term infants only, without accounting for palivizumab eligible infants protection.
Abbreviations: ER, emergency room; ICU, intensive care unit; MV, mechanical ventilation; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; SoP, standard of practice.
Conclusion:
“Consistent with the estimated greater benefits with the Nirsevimab strategy, the NNI to avoid an RSV-LRTD-related event was consistently lower compared to the alternative prophylactic options”
- Kieffer A, Ghemmouri M, Soudani S. Comparison of the public health impact of RSV disease prevention options for infants: a static decision model of the US birth cohort. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2025;24(1):1086-1098. doi:10.1080/14760584.2025.2591816 (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/41252531/)
- Esposito S, et al. Front Immunol 2022;13:880368
- Beyfortus SmPC. Available at: https://pro.campus.sanofi/dam/Portal/UAE/Products/beyfortus/pdf/Beyfortus-SmPC.pdf
- Abrysvo SmPC. Available at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/abrysvo-epar-product-information_en.pdf [accessed April 2025].
Rapid scientific advice on protecting infants against respiratory syncytial virus disease for the European 2025/26 winter season
Published on: November 2025
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Publication assessed the different immunization interventions to mitigate the impact of RSV disease in infants published on November 2025
MAb (nirsevimab) vs Maternal Immunization comparison:
|
Aspect |
Nirsevimab (mAb) |
Maternal Immunization |
|
Efficacy |
76–86% against RSV hospitalization, Real-world impact up to 95% reduction |
~74% against severe RSV; ~54–78% against hospitalization |
|
Duration of Protection |
~5–6 months (covers RSV season) |
Up to 6 months post-birth Babies born out of season will NOT be protected as they enter the RSV season. |
|
Safety |
Strong profile; no major concerns |
Generally safe; ongoing monitoring for preterm birth risk |
|
Coverage & Uptake |
High (>80% in pilots; Spain 90%) |
Lower (France 27%, UK 55%) |
MAT-BH-2600004/V1/January2026