Jump to:
Aldurazyme showed improved respiratory function and walking distance in patients with Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPS I).1
Aldurazyme improved pulmonary function (FVC) in patients with MPS I1,a,b
In the 26-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients treated with Aldurazyme (n=22) experienced a mean 4-point increase in percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC) compared with those receiving placebo (n=23) (median difference 2.0 [95% CI:0.4, 7] p=0.02).1
Study 1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 45 patients with MPS I, aged 6 to 43 years, including 1 patient with the Hurler form, 37 patients with Hurler-Scheie form, and 7 patients with Scheie form of MPS I. All patients had a baseline percent predicted FVC less than or equal to 77%. Patients received Aldurazyme at 0.58 mg/kg of body weight once weekly or placebo once weekly for 26 weeks. All patients were treated with antipyretics and antihistamines prior to each infusion. The primary efficacy outcome assessments were percent predicted FVC and distance walked in 6 minutes (6-MWT).1
Mean change over time in FVC values2
- Mean pretreatment baseline for FVC (percent of a predicted normal) was 48 ± 15 for the Aldurazyme arm and 54 ± 16 for the placebo arm1
- Mean Week 26 FVC was 50 ± 17 for the Aldurazyme arm and 51 ± 13 for the placebo arm1
aThe risks and benefits of treating mildly affected patients with the Scheie form have not been established.
bAldurazyme has not been evaluated for its effects on the central nervous system manifestations of the disorder.
cWilcox Rank Sum Test on median of difference.
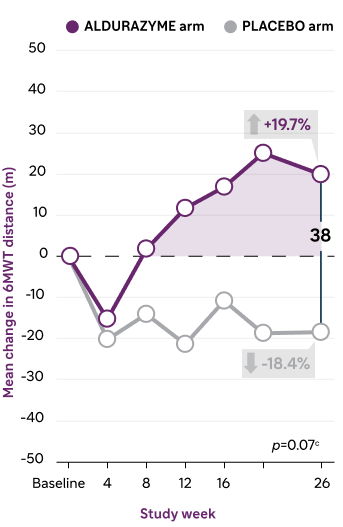
Aldurazyme improved walking distance (6-MWT) in patients with MPS I1,a,b
In the 26-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients treated with Aldurazyme (n=22) showed a mean 38-meters increase in distance walked (as measured by the 6-MWT) compared with those receiving placebo (n=23) (median difference 39 [95% CI: -2.0, 79.0] p=0.07).1,3
Study 1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 45 patients with MPS I, ages 6 to 43 years old, including 1 patient with the Hurler form, 37 patients with Hurler-Scheie form, and 7 patients with Scheie form of MPS I. All patients had a baseline percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC) less than or equal to 77%. Patients received Aldurazyme at 0.58 mg/kg of body weight once weekly or placebo once weekly for 26 weeks. All patients were treated with antipyretics and antihistamines prior to each infusion. The primary efficacy outcome assessments were percent predicted FVC and distance walked in 6 minutes (6-MWT).
Mean change over time in distance walked3
.png)
- Mean pretreatment baseline for the 6-MWT distance in meters was 319 ± 131 for the Aldurazyme arm and 367 ± 114 for the placebo arm1
- Mean week 26 6-MWT distance in meters was 339 ± 127 for the Aldurazyme arm and 348 ± 129 for the placebo arm1
aThe risks and benefits of treating mildly affected patients with the Scheie form have not been established.
bAldurazyme has not been evaluated for its effects on the central nervous system manifestations of the disorder.
cWilcox Rank Sum Test on median of difference.
Study 2 was a 182-week, open-label, uncontrolled extension study of all 45 patients who completed Study 1. Patients received Aldurazyme at 0.58 mg/kg body weight once weekly.
For patients treated with Aldurazyme, the mean increase in the 6‑MWT distance was maintained for an additional 182 weeks through the completion of Study 2.1
Aldurazyme decreased urinary glycosaminoglycan (GAG) level by 54%3,a,b
Results from a randomized, double‑blind, placebo-controlled study of 45 MPS I patients (aged 6 to 43 years) measuring mean change over time in urinary GAG level (n=22 and 23 for the placebo group and n=21 and 22 for the Aldurazyme group, respectively, at baseline and week 26).
Study 1 Design
Study 1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 45 patients with MPS I, ages 6 to 43 years old, including 1 patient with the Hurler form, 37 patients with Hurler-Scheie form, and 7 patients with Scheie form of MPS I. All patients had a baseline percent predicted forced vital capacity (FVC) less than or equal to 77%. Patients received Aldurazyme at 0.58 mg/kg of body weight once weekly or placebo once weekly for 26 weeks. All patients were treated with antipyretics and antihistamines prior to each infusion. The primary efficacy outcome assessments were percent predicted FVC and distance walked in 6 minutes (6-MWT).
Study 2 Design
Study 2 was a 182-week, open-label, uncontrolled extension study of all 45 patients who completed Study 1. Patients received Aldurazyme at 0.58 mg/kg body weight once weekly.
Mean change over time in urinary glycosaminoglycan (GAG) levels
- Urinary GAG levels decreased in patients treated with Aldurazyme compared to placebo. No patients in the group receiving Aldurazyme reached the normal range for urinary GAG levels during this six-month study1
aThe risks and benefits of treating mildly affected patients with the Scheie form have not been established.
bAldurazyme has not been evaluated for its effects on the central nervous system manifestations of the disorder.
cWilcox Rank Sum Test on median of difference.
At the end of Study 2, the decrease in mean urinary GAG was similar to the decrease in urinary GAG reported in the Aldurazyme-treated patients at the end of Study 1.1
The relationship of urinary GAG to other measures of clinical response has not been established.1
6-MWT=six-minute walk test; FVC=forced vital capacity; GAG=glycosaminoglycan; MPS I=mucopolysaccharidosis type I.
Indication
References: 1. Aldurazyme (laronidase). Prescribing Information. Sanofi. 2. Data on file. Genzyme Corporation. 3.Wraith JE et al. J Pediatr. 2004;144(5):581-588.