THE ONLY HIGH-DOSE INFLUENZA VACCINE SHOWN TO PROTECT AGAINST FLU AND ITS COMPLICATIONS1-3*†

Fluzone High-Dose is among the flu vaccines preferentially recommended by ACIP for those aged 65+ vs unadjuvanted standard-dose flu vaccines.4
WHY CHOOSE FLUZONE HIGH-DOSE FOR YOUR OLDER PATIENTS AGED 65+
FLUZONE HIGH-DOSE PROVIDES 4x THE ANTIGEN
- In studies of older patients, higher hemagglutinin (HA) content in influenza vaccines has been associated with higher protective influenza titers5
- Fluzone High-Dose contains 60 micrograms (mcg) of HA per strain compared to 15 mcg of HA per strain in a standard-dose influenza vaccine5
MORE ANTIGEN, MORE PROTECTION
- Compared to younger patients, adults aged 65+ are at increased risk for severe influenza-associated illness and hospitalization4
- Higher dose flu vaccines are preferentially recommended by ACIP over unadjuvanted standard dose vaccines for eligible patients aged 65+4

Contains 4x THE ANTIGEN of standard-dose flu vaccines1,2†

The only flu vaccine to deliver SUPERIOR PROTECTION VS STANDARD DOSE in a randomized controlled trial of patients 65+1,2*

Real-world evidence in hospitalizations across 12 FLU SEASONS and 45+ MILLION PEOPLE in randomized and observational studies3‡
*In an RCT conducted in 2011-2012 and 2012-2013 in approximately 32,000 adults 65+, Fluzone High-Dose was 24% (95% CI: 10, 37) more effective (rVE) against influenza due to ANY lab-confirmed circulating strains than standard-dose Fluzone. The prespecified statistical superiority criterion for the primary endpoint (lower limit of 2-sided 95% CI of the vaccine efficacy of Fluzone High-Dose relative to Fluzone >9.1%) was met.1,2
†Fluzone High-Dose contains 60 mcg of HA per strain vs 15 mcg of HA per strain in a standard-dose influenza vaccine.2
‡Analysis included studies conducted over 12 influenza seasons (2009-2010 to 2019-2020, and 2021-2022) in adults 65+.3

PIVOTAL TRIAL:
FLUZONE HIGH-DOSE CONTAINS 4x THE ANTIGEN AND REDUCED FLU CASES BY 24% VS A STANDARD-DOSE FLU VACCINE IN A CLINICAL TRIAL OF ADULTS AGED 65+1,2*†
Study Design
- 1:1 RCT to evaluate Fluzone High-Dose vs standard-dose Fluzone1,2
- Study population: 31,803 adults aged 65+ during the influenza seasons 2011-2012 and 2012-20131,2
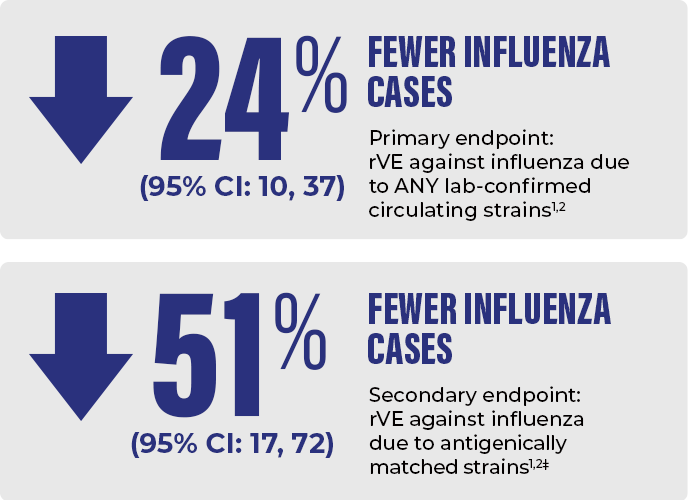
*Results from a study evaluating Fluzone High-Dose (trivalent formulation) vs Fluzone (standard-dose trivalent formulation). The prespecified statistical superiority criterion for the primary endpoint (lower limit of 2-sided 95% CI of the vaccine efficacy of Fluzone High-Dose relative to Fluzone >9.1%) was met.1,2
†Fluzone High-Dose contains 60 mcg of HA per strain vs 15 mcg of HA per strain in a standard-dose influenza vaccine.2
‡Modified CDC-defined influenza-like illness was based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) surveillance network definition of an influenza-like illness and was defined as a respiratory illness with cough or sore throat, concurrent with a temperature above 37.2 °C. Influenza was culture-confirmed.2
ACIP=Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices; CI=confidence interval; RCT=randomized controlled trial; rVE=relative vaccine efficacy; RWE=real-world evidence.

REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE:
EVALUATED AGAINST STANDARD-DOSE FLU VACCINES OVER 12 SEASONS3

Study Design3*
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and observational studies to evaluate the rVE of Fluzone High-Dose vs standard-dose influenza vaccines against influenza-associated outcomes in more than 45 million adults aged 65+
- Analysis included studies conducted over 12 influenza seasons (2009-2010 to 2019-2020, and 2021-2022)
- The dominant strains were A/H3N2 and A/H1N1 in 8 and 4 of the seasons studied, respectively
- In 8 of the 12 seasons, there was a mismatch between vaccine and circulating strains
Study Limitations3
- High degree of statistical heterogeneity observed in several of the pooled rVE estimates
- Inclusion of unmeasured confounders, such as health-seeking behavior or selection bias, that could affect the findings of the observational studies
*The study was supported by Sanofi; findings of the study were derived from manuscripts of 21 published studies in the public domain.3
FLUZONE HIGH-DOSE PREVENTED MORE INFLUENZA COMPLICATIONS VS STANDARD-DOSE VACCINES3
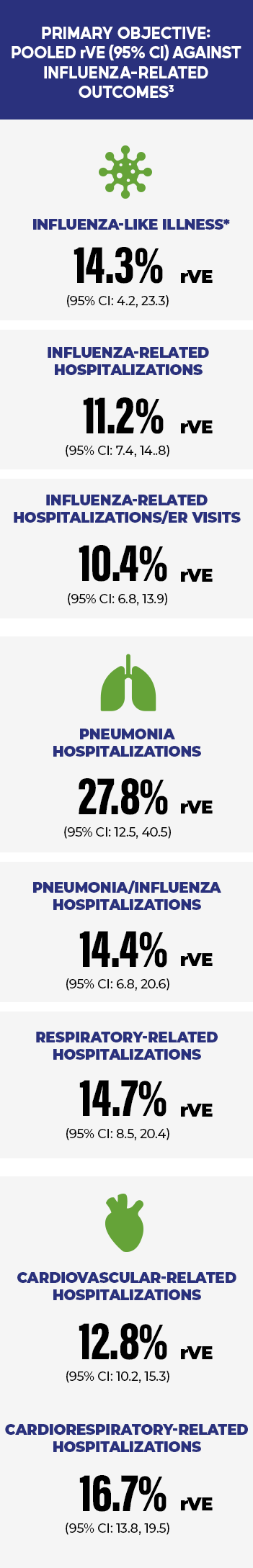
*Defined as visits with a rapid influenza diagnostic test followed by prescription of antiviral medication.3
ER=emergency room; rVE=relative vaccine effectiveness.

PHASE 3 IMMUNOGENICITY AND SAFETY STUDY
SAFETY PROFILE COMPARED TO STANDARD-DOSE FLU VACCINES5
Solicited systemic adverse reactions and solicited injection-site reactions were slightly more frequent after vaccination with Fluzone High-Dose as compared with a standard-dose influenza vaccine.5
Study Design
- A Phase 3 controlled study in which 3876 adults aged 65+ were randomized 2:1 to receive Fluzone High-Dose or Fluzone (standard dose) during the influenza season of 2006-20075*
Adverse Reactions (Within 7 Days)5
- Study population values for each solicited adverse reaction are provided for the Fluzone High-Dose cohort, then the standard-dose Fluzone cohort
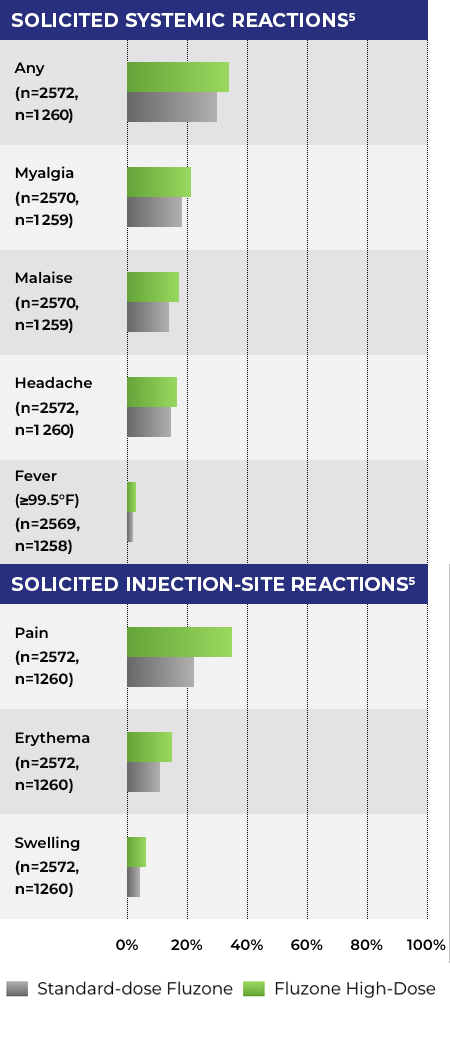
*Fluzone High-Dose (trivalent formulation) was evaluated against Fluzone (standard-dose trivalent formulation).5
Important Safety Information
References: 1. Fluzone High-Dose. Prescribing Information. Sanofi Pasteur Inc. 2. DiazGranados CA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(7):635-645. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1315727 3. Lee JKH, et al. Vaccine X. 2023;14:100327. doi:10.1016/j.jvacx.2023.100327 4. Grohskopf LA, et al. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2024;73(5):1-25. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7305a1 5. Falsey AR, et al. J Infect Dis. 2009;200(2):172-180. doi:10.1086/599790
