There are no clinically meaningful differences between MERILOG (insulin aspart-szjj) injection 100 Units/mL and NovoLog®.
The PK profiles of MERILOG (insulin aspart-szjj) injection 100 Units/mL & NovoLog were superimposable in 30 subjects with T1D1
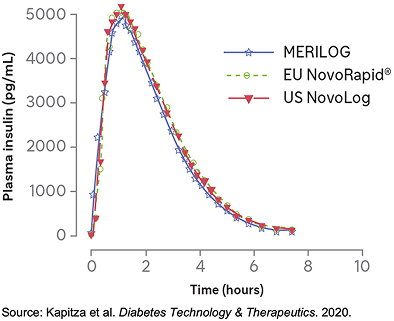
MERILOG, US NovoLog, and EU NovoRapid* achieved similar plasma concentrations, indicating fast absorption with a rapid onset of action1
- MERILOG and NovoLog were each administered SC as a single 0.3-U/kg dose in a euglycemic clamp study1,2
- The 90% CIs for the pairwise treatment ratios of INS-Cmax, INS-AUClast, and INS-AUCinf were entirely within the predefined equivalence interval (0.80-1.25), thus demonstrating equivalent PKs for both aspart formulations1
The clinical relevance of PK results is unknown.
*non-U.S.-approved biological product
Phase 1 PK/PD Study Design: A single-center, randomized, double-blind, 3-period, 6-sequence, euglycemic clamp crossover study conducted in 30 adult male subjects with T1D. Subjects received 0.3 U/kg of each treatment (MERILOG, NovoLog, or a non–US-approved insulin aspart) under fasted conditions and underwent a 12-h euglycemic clamp technique to assess PK/PD activity for up to 12 h. The primary PK/PD endpoints were the areas under the plasma insulin concentration–time curve from time zero to INS-AUClast and extrapolated to INS-AUCinf, INS-Cmax, and the areas under the body weight-standardized
GIR-AUC0-12h among the 3 treatments.1
The study population only included males. Restriction of studies to males alone is considered acceptable, as insulin sensitivity in women may vary during the menstrual cycle.2
The PD Profiles of MERILOG & NovoLog Were Similar, Displaying Short Time–Action Profiles1
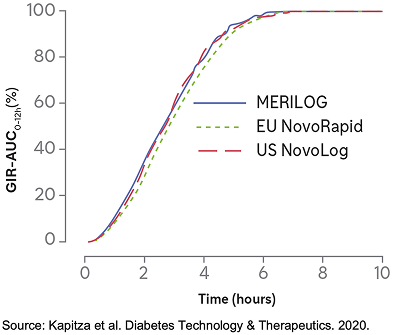
The overall PD profile of MERILOG was similar to those of US NovoLog and EU NovoRapid1,*
- MERILOG and NovoLog were each administered SC as a single 0.3-U/kg dose in a euglycemic clamp study1,2
- The extent of the glucose-lowering effect was similar between the treatments, with 90% CIs and 95% CIs for the pairwise treatment ratio entirely within the predefined interval of 0.80-1.25, demonstrating the equipotency of MERILOG and NovoLog1
The clinical relevance of PD results is unknown.
*non-U.S.-approved biological product
Phase 1 PK/PD Study Design: A single-center, randomized, double-blind, 3-period, 6-sequence, euglycemic clamp crossover study conducted in 30 adult male subjects with T1D. Subjects received 0.3 U/kg of each treatment (MERILOG, NovoLog, or a non–US-approved insulin aspart) under fasted conditions and underwent a 12-h euglycemic clamp technique to assess PK/PD activity for up to 12 h. The primary PK/PD endpoints were the areas under the plasma insulin concentration–time curve from time zero to INS-AUClast and extrapolated to INS-AUCinf, INS-Cmax, and the areas under the body weight-standardized
GIR-AUC0-12h among the 3 treatments.1
The study population only included males. Restriction of studies to males alone is considered acceptable, as insulin sensitivity in women may vary during the menstrual cycle.2
MERILOG Was Noninferior to NovoLog as Demonstrated by Similar Changes in A1C From Baseline to Week 263,4
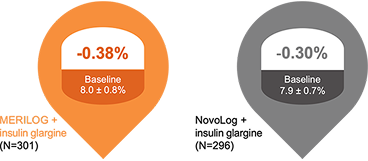
Demonstrated noninferiority3
26 weeks
LS mean difference (± SE) –0.08 ± 0.059
[95% CI, –0.192 to 0.039]
The upper bound of the 95% CI of the between-group difference was lower than the predefined noninferiority margin of 0.3%, demonstrating noninferiority between MERILOG and NovoLog.
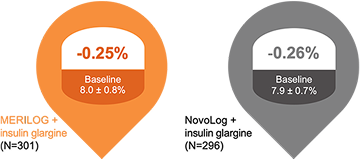
Sustained long-term efficacy4
52 weeks
LS mean difference (± SE) –0.01 ± 0.082 [95% CI, –0.146 to 0.173]
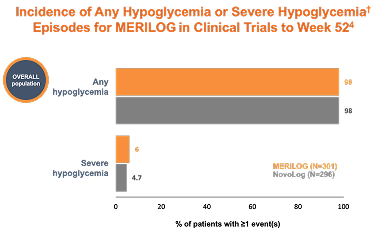
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event for insulin-containing therapies
-
Hypoglycemia was reported by similar percentages of patients in the MERILOG and NovoLog groups across all categories of hypoglycemia (96.7% and 96.3% in all categories with severe hypoglycemia accounting for 4.0% and 3.4%, respectively)
-
Safety and tolerability including AIA (anti-insulin aspart antibody) and NAb (neutralizing antibody) responses (incidence and prevalence) and AEs, including hypersensitivity events (3.7% and 3.7%, respectively) and injection site reactions (0.7% and 1.4%, respectively) were similar for MERILOG and NovoLog.
Phase 3 GEMELLI 1 Study Design: An open-label, multicenter, parallel-group, phase 3 clinical trial conducted in 597 adult subjects with T1D or T2D. Subjects were randomized 1:1 to receive 100 U/mL (dose range 1-80 U) of the treatment drug (MERILOG or NovoLog) SC before meals with Gla-100 QD up to Week 52. The primary endpoint was the change in A1C from baseline to Week 26. The secondary endpoints were the percentage of study participants with A1C <7.0% (<53 mmol/mol), changes in FPG from baseline to Week 26 and Week 52, changes in the mean 24-h plasma glucose concentration from baseline to Week 26 and Week 52, and PPG excursions from baseline to Week 26 and Week 52. The 6-month extension aimed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of MERILOG during the entire 12-month period.3-5
- Limitations: The open-label design is a potential limitation of this study; blinding was not possible as the devices used to administer the treatments differed.3
See GEMELLI 1 26 week Study Results3
See GEMELLI 1 52-week Study Results4
†Hypoglycemia is defined as a measurable glucose concentration <70 mg/dL (<3.9 mmol/L) but ≥54 mg/dL (≥3.0 mmol/L). Severe hypoglycemia is defined as a severe event characterized by altered mental and/or physical functioning that requires assistance from another person for recovery, irrespective of glucose level.6
A1C, Hemoglobin A1c; CI, Confidence Interval; EU, European Union; FPG, Fasting Plasma Glucose; GIR-AUC, Glucose Infusion Rate Area Under the Curve; INS-AUCinf, Insulin Area Under the Curve extrapolated to infinity; INS-AUClast, Insulin Area Under the Curve to last measurable concentration; INS-Cmax, Maximum Plasma Concentration of Insulin; LS, Least Squares; PD, Pharmacodynamics; PK, Pharmacokinetics; QD, Once Daily; SAEs, serious adverse events; SC, Subcutaneous; SE, Standard Error; T1D, Type 1 Diabetes; TEAEs, treatment-emergent adverse events; US, United States.
Important Safety Information
References
- Kapitza C, Nosek L, Schmider W, Teichert L, Nowotny I. Single-Dose Euglycemic Clamp Study Demonstrating Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Similarity Between SAR341402 Insulin Aspart and US- and EU-Approved Versions of Insulin Aspart in Subjects with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(4):278-284.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT03202875. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03202875. Accessed October 28, 2025.
- Garg SK, Wernicke-Panten K, Wardecki M, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Aspart Biosimilar SAR341402 Versus Originator Insulin Aspart in People with Diabetes Treated for 26 Weeks with Multiple Daily Injections in Combination with Insulin Glargine: A Randomized Open-Label Trial (GEMELLI 1). Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(2):85-95.
- Garg SK, Wernicke-Panten K, Wardecki M, et al. Safety, Immunogenicity, and Glycemic Control of Insulin Aspart Biosimilar SAR341402 Versus Originator Insulin Aspart in People with Diabetes Also Using Insulin Glargine: 12-Month Results from the GEMELLI 1 Trial. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2020;22(7):516-526.
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT03211858. Available at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03211858. Accessed October 28, 2025.
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S83-S96.

