Jump to:
Cerezyme improves certain bone parameters in adults and children with Gaucher disease type 1.1-5
Bone parameters have been assessed across several studies2,6
A multicenter, non-inferiority, double-blind, active-controlled, randomized trial of 30 patients with Gaucher disease type 1. Fifteen patients (12 adults, 3 children ≥12 years) started Cerezyme for injection at 60 U/kg every 2 weeks and 15 patients (11 adults, 4 children ≥12 years) started alglucerase 60 U/kg every 2 weeks. The primary outcome measures were spleen and liver volumes (as estimated by CT or MRI), hemoglobin level, and platelet count.
The 20-year International Collaborative Gaucher Group (ICGG) Gaucher Registry study is a retrospective, observational, single-arm study of patients with Gaucher disease type 1 who were treated with Cerezymea for about 20 years.
Cerezyme: Effect on bone mineral density (BMD), bone pain, and bone crises1-3
An overview: Cerezyme studies for bone manifestations in Gaucher disease type 1
| Description | Time frame | BMD | Bone pain | Bone crisis |
|
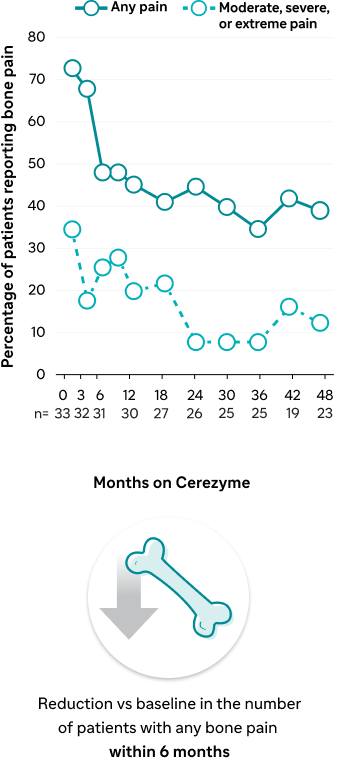
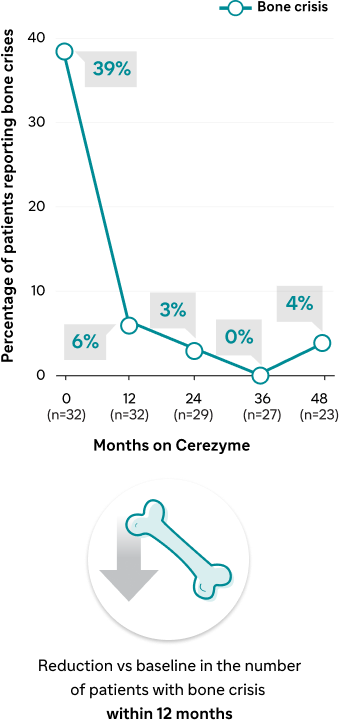
A prospective, non-randomized, open-label, 48-month study of the effect of Cerezyme on Gaucher-related bone disease1 | Results within 12 months | Trend toward improvements in lumbar spine and femoral neck BMD within 12 months1 | Reduction within 6 months1 | Reduction of bone crisis within 12 months1 |
| Results up to 48 months | Improved lumbar spine and femoral neck BMD over 48 months1 | Continued reduction over 48 months1 | Continued reduction over 48 months1 | |
|
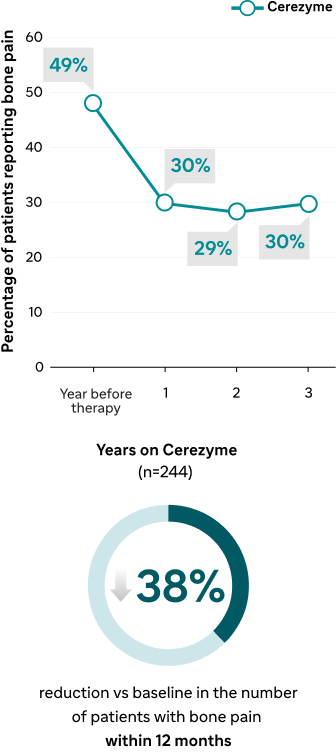
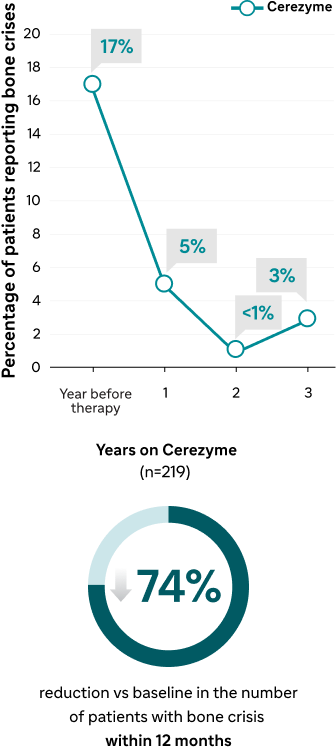
ICGG Gaucher Registry analyses of the effect of Cerezyme on Gaucher-related bone disease3,4 | Results within 12 months | 38% reduction within 12 months4 | 74% reduction within 12 months4,a | |
| Results up to 8 years | Improved lumbar spine BMD after 8 years3 | Reduction over 3 years4 | Reduction over 3 years4 |
aPercentage changes from baseline were calculated by dividing the change from baseline by the baseline value and multiplying by 100.
ICGG=International Collaborative Gaucher Group.
48-month, long-term prospective study1
Study design1
Prospective, nonrandomized, open-label, single-cohort, multicenter, 48-month study design
The exclusion criteria included perimenopausal status, major concurrent disorders, nonambulatory status, more than 1 joint replacement, prior enzyme therapy (enrollment was permitted up to 12 weeks after first infusion of enzyme), gene therapy, bone marrow transplantation, and use of medications known to affect bone homeostasis, including bisphosphonates.
aHistory of at least 1 bone crisis, osteoarticular necrosis, medullary infarction, lytic lesions, pathological fractures or fractures related to Gaucher disease, marrow infiltration with a unilateral Rosenthal MRI score ≥3, bone density by DXA or quantitative computerized tomography scan Z-score ≤1.5, or Erlenmeyer flask deformity. Bone crisis was defined as pain with acute onset requiring immobilization of the affected area and narcotics for the relief of pain, and may be accompanied by one or more of the following: periosteal elevation, elevated white blood cells, fever, or debilitation of >3 days. Bone pain was assessed by patient report on a 6-point scale: None, very mild, mild, moderate, severe, or extreme.
DXA=dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Long-term effect of Cerezyme on BMD1
Improvement in DXA bone density measurement following Cerezyme
Effect of Cerezyme on the occurrence of bone pain and bone crises1
Bone pain occurrence
Bone crises occurrence
Safety1
- The most common adverse events were chills, flushing, and arthralgia, each reported in 4 patients (12%)
- One patient withdrew from the study because of a severe infusion reaction, including anxiety, chest pain, hypertonia, chills, tachycardia, and vomiting, from which he recovered without sequelae
Long-term registry studies
8-year ICGG Gaucher Registry analysis: Study parameters2
An observational, retrospective analysis in adults (men aged 18 to 70 years, women aged 18 to 50 years) enrolled in the ICGG Gaucher Registry for whom lumbar spine BMD measurements were available.
Patient population:
- BMD data with up to 8 years of follow-up were analyzed for 160 patients who received no ERT and 342 patients treated with ERT
- BMD was assessed by DXA of the lumbar spine. Data from patients reporting treatment with bisphosphonates were excluded from this analysis. Patients with doses outside of the range 5–75 U/kg/2 weeks were excluded
Analysis limitations:
- Information entry is voluntary and not all the data on every parameter are available for every patient in the registry. The ICGG Registry includes patients with a variable range of disease status and management
Cerezyme impact on BMD over 8 years2
DXA Z-score in patients with no Cerezyme
DXA Z-score in Cerezyme patients over 8 years
- Cerezyme dosing should be individualized to each patient6
- The recommended dosage of Cerezyme ranges from 2.5 U/kg 3 times a week to 60 U/kg once every 2 weeks6
- Titrate the dosage based on disease severity and therapeutic goals for the patient6
4-year ICGG Gaucher Registry analysis: Study parameters3
This retrospective analysis used data from the ICGG Gaucher Registry on patients with bone crisis and/or bone pain data for 3 years prior to Cerezyme, and each year for 3 years after the start of Cerezyme. The year before treatment was considered to be baseline. Data on bisphosphonate use were not available.
Definitions:
- Bone crisis is defined as pain with acute onset that requires immobilization of the affected area and narcotics for the relief of pain, and may be accompanied by one or more of the following: periosteal elevation, elevated white blood cell count, fever, or debilitation >3 days. This definition excludes fracture and osteomyelitis
- Bone pain is defined as pain attributable to Gaucher disease experienced during the 30-day period preceding the report
Analysis limitations:
- Information entry is voluntary and not all the data on every parameter are available for every patient in the registry. The ICGG Registry includes patients with a variable range of disease status and management
Long-term effect of Cerezyme on the occurrence of bone pain and bone crises3
Bone pain
Bone crises
Indication
References: 1. Sims KB, Pastores GM, Weinreb NJ, et al. Improvement of bone disease by imiglucerase (Cerezyme) therapy in patients with skeletal manifestations of type 1 Gaucher disease: results of a 48-month longitudinal cohort study. Clin Genet. 2008;73(5):430-440. 2. Wenstrup RJ, Kacena KA, Kaplan P, et al. Effect of enzyme replacement therapy with imiglucerase on BMD in type 1 Gaucher disease. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(1):119-126. 3. Charrow J, Dulisse B, Grabowski GA, Weinreb NJ. The effect of enzyme replacement therapy on bone crisis and bone pain in patients with type 1 Gaucher disease. Clin Genet. 2007;71(3):205-211. 4. Weinreb NJ, Camelo JS Jr, Charrow J, et al. Gaucher disease type 1 patients from the ICGG Gaucher Registry sustain initial clinical improvements during twenty years of imiglucerase treatment. Mol Genet Metab. 2021;132(2):100-111. 5. Andersson H, Kaplan P, Kacena K, Yee J. Eight-year clinical outcomes of long-term enzyme replacement therapy for 884 children with Gaucher disease type 1. Pediatrics. 2008;122(6):1182-1190. 6. Cerezyme (imiglucerase). Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA. 7. Grabowski GA, Barton NW, Pastores G, et al. Enzyme therapy in type 1 Gaucher disease: comparative efficacy of mannose-terminated glucocerebrosidase from natural and recombinant sources. Ann Intern Med. 1995;122(1):33-39.
