of adult patients were at high risk for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) at baseline1
of adult patients had normal uric acid levels (≤7.5 mg/dL) at baseline1
Adult patients meeting at least 1 of the following criteria were enrolled in the pivotal trial1:
|
HIGH RISK1-3 |
|
Aggressive lymphoma/leukemia (defined by REAL)
|
|
AML |
|
Elevated plasma uric acid levels (>7.5 mg/dL) at baseline |
|
High-grade MDS with >10% bone marrow blast involvement |
|
CML in blast crisis |
| INTERMEDIATE (POTENTIAL) RISK1 |
|
Aggressive lymphoma/leukemia, not limited to the REAL definition, with LDH ≥2x the upper limit of normal
|
| Any stage III to IV aggressive lymphoma or leukemia |
|
Stage I or II aggressive disease with bulky lymph node/tumor (>5 cm) involvement
|
ELITEK Efficacy and Safety Flashcard
Use this efficacy and safety flashcard to see the head-to-head pivotal trial data between ELITEK and allopurinol
DOWNLOAD NOW
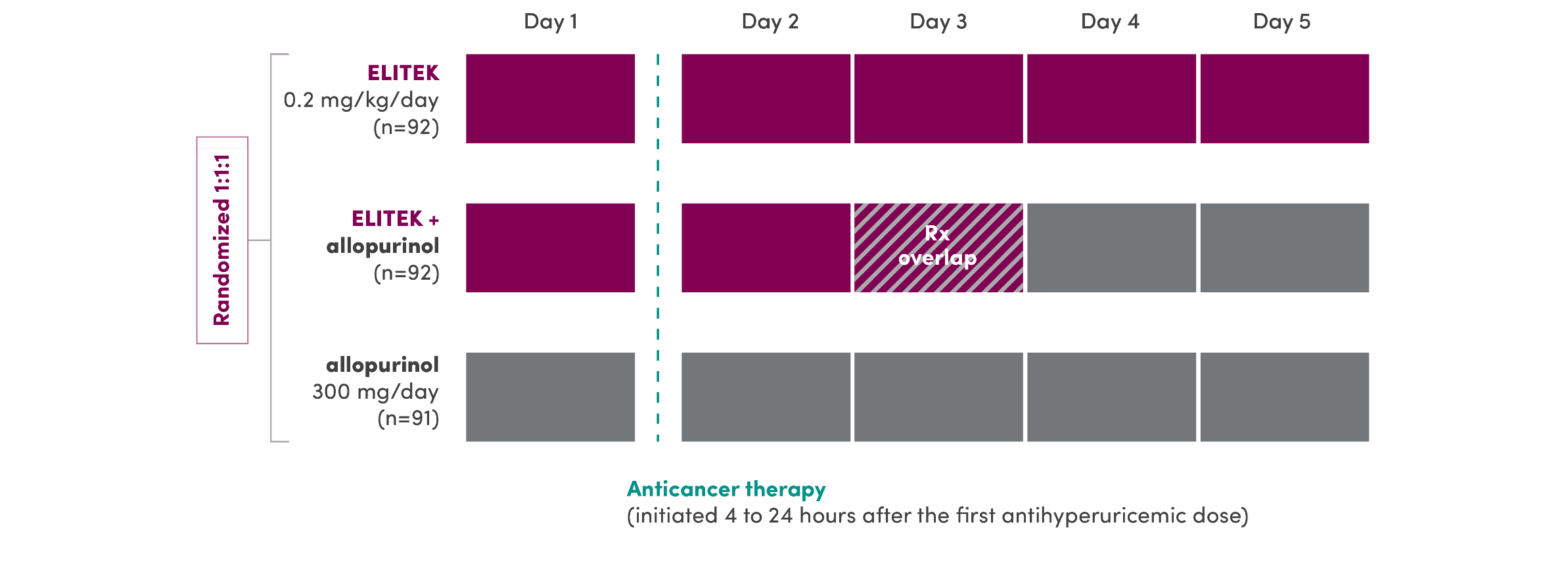
Antihyperuricemic therapy in all 3 arms was initiated prior to anticancer therapy1,4
- Phase 3: randomized, multicenter, open-label study in adult patients (N=275) with leukemia, lymphoma, and solid tumor malignancies at risk for hyperuricemia and TLS
- Primary endpoint: response rate defined as the proportion of adult patients with plasma uric acid levels maintained at ≤7.5 mg/dL between 3 and 7 days after initiation of antihyperuricemic treatment
ADULT PIVOTAL TRIAL DESIGN1,4
See how these adults responded to treatment with ELITEK
AML=acute myeloid leukemia; CLL=chronic lymphocytic leukemia; CML=chronic myeloid leukemia; DLBCL=diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; LDH=lactate dehydrogenase; MDS=myelodysplastic syndrome; REAL=Revised European American Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms.
References: 1. Cortes J, Moore JO, Maziarz RT, et al. Control of plasma uric acid in adults at risk for tumor lysis syndrome: efficacy and safety of rasburicase alone and rasburicase followed by allopurinol compared with allopurinol alone—results of a multicenter phase III study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28(27):4207-4213. 2. Jakić-Razumović J, Aurer I. The World Health Organization classification of lymphomas. Croat Med J. 2002;43(5):527-534. 3. Nicolaides C, Dimou S, Pavlidis N. Prognostic factors in aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Oncologist. 1998;3(3):189-197. 4. ELITEK [prescribing information]. NJ: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC.