NUVAXOVID has proven efficacy in a randomized clinical trial of over 25,000 patients1,2
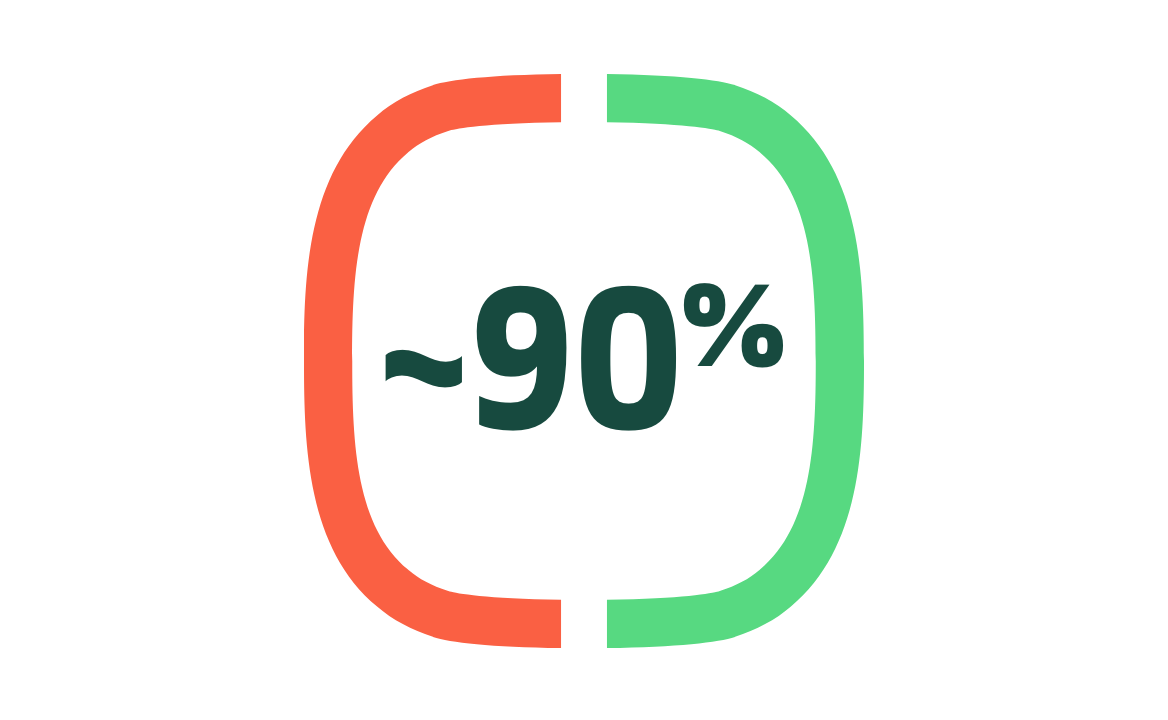
Efficacy preventing COVID-19 in all patients1
Primary endpoint: efficacy in preventing PCR-confirmed symptomatic mild, moderate, or severe COVID-19 from 7 days after the second dose.
(95% CI: 82.5, 93.8; P<0.001) N=25,510
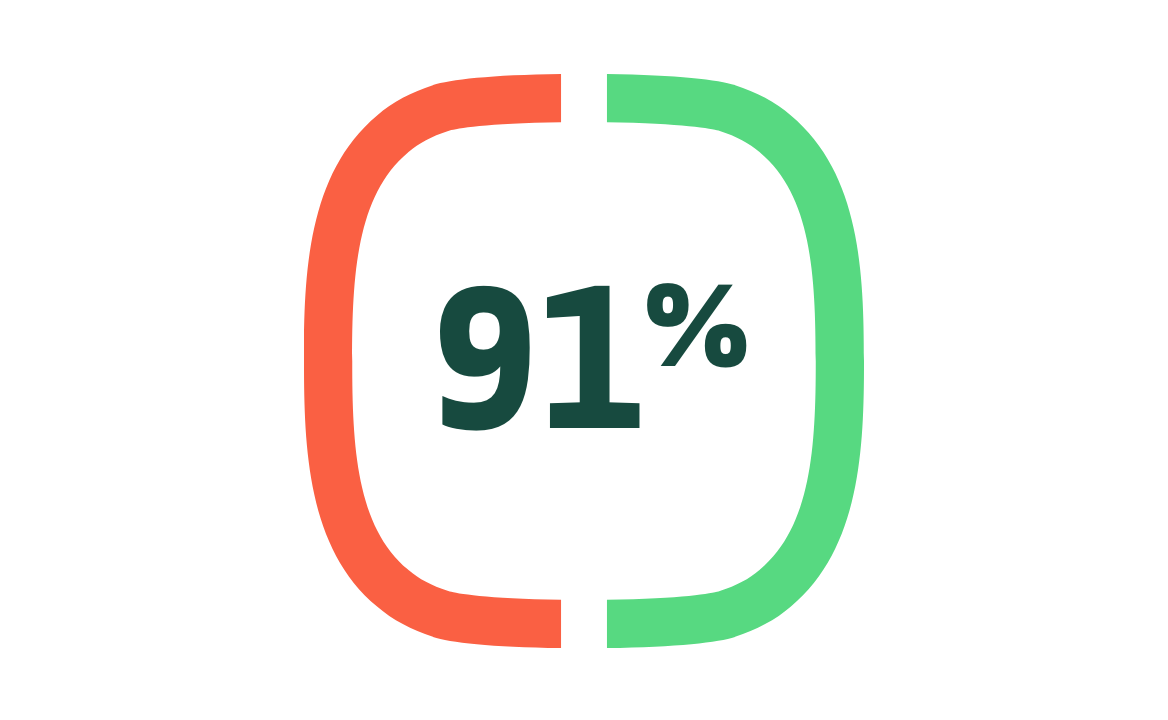
Efficacy preventing COVID-19 in high-risk patients1,2
Subgroup analysis: efficacy in protection against COVID-19 in high-risk patients*
(95% CI: 83.6, 95.0) N=24,230
NUVAXOVID provided powerful protection against moderate-to-severe COVID-192

Protection from moderate-to-severe COVID-191,2
Secondary endpoint: efficacy in preventing moderate-to-severe disease from then-circulating strains of virus.
(95% CI: 87.0, 100.0) N=25,452

Protection from COVID-19 hospitalization3
Post hoc analysis: efficacy against hospitalization due to then-circulating strains of virus.
(95% CI: 83.1, 100.0) N=25,482
NUVAXOVID may not protect all patients.1
Pivotal Trial Study Design1,2:
- Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, observer-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial evaluating efficacy and safety in 29,943 adults aged 18 and older
- Participants were stratified by age (18 to 64 years and ≥65 years) and assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive NUVAXOVID or placebo
- Data based on strains circulating at time of study (December 2020 through April 2021)
- Moderate disease was defined as high fever and objective evidence of lower respiratory tract infection. Severe disease was defined as clinically significant tachypnea, tachycardia, or hypoxia; receipt of intensive respiratory support; major dysfunction of one or more organ systems; admission to an intensive care unit; or death.
Subgroup Analysis1:
Of the study participants in the PP-EFF Analysis Set, 95.2% were at high risk for COVID-19 due to living or working conditions involving known frequent exposure to SARS CoV-2, comorbidities (chronic lung disease, cardiovascular disease, chronic liver disease, severe obesity, and diabetes), or age ≥65 years
Post Hoc Analysis3:
Two post-hoc analyses were conducted, the per-protocol efficacy analysis and the expanded efficacy analysis. The latter removed a per-protocol requirement for central laboratory testing.
In the per-protocol efficacy analysis of the Phase 3 trial including 25,482 participants, 4 hospitalizations were identified—0 among NUVAXOVID COVID-19 vaccine recipients and 4 among placebo—resulting in a vaccine efficacy against hospitalization of 100% (95% CI: 28.8, 100.0)
Post Hoc Analysis Limitations3:
- Vaccine efficacy estimates impacted by low number of events (ie, hospitalizations)
- Pandemic-era restrictions successfully reducing infections and hospitalizations during the study
- The exclusion of key demographics, such as participants with certain underlying health conditions (ie, some immunocompromised populations) may not have fully reflected the general population
- The limited duration of the study window did not permit assessment of long-term vaccine efficacy
*Participants at overall high risk for COVID-19 included those 65 years of age or older and those of any age with chronic health conditions or an increased risk for COVID-19 because of work or living conditions.2
Order NUVAXOVID today and offer your patients the powerful protection of this protein-based, non-mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.1
INDICATION
References
1. NUVAXOVID. Prescribing Information. Novavax, Inc. 2. Dunkle LM, Kotloff KL, Gay CL, et al; 2019nCoV-301 Study Group. Efficacy and safety of NVX-CoV2373 in adults in the United States and Mexico. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(6):531-543. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116185 3. Marchese AM, Zhou X, Kinol J, et al. NVX-CoV2373 vaccine efficacy against hospitalization: a post hoc analysis of the PREVENT-19 phase 3, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Vaccine. 2023;41(22):3461-3466. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.04.054
