Toujeo® a longer-acting basal insulin with proven A1C reduction and demonstrated safety profile across EDITION pivotal trials1-4
In a PK/PD study: A longer-lasting, glucose-lowering effect vs Lantus®5,6
These PK/PD data do not support a comparison of the safety or efficacy of Toujeo and Lantus.
Time course effect following product administration (N=30)5,6
Once-daily Toujeo® should be injected at the same time each day.
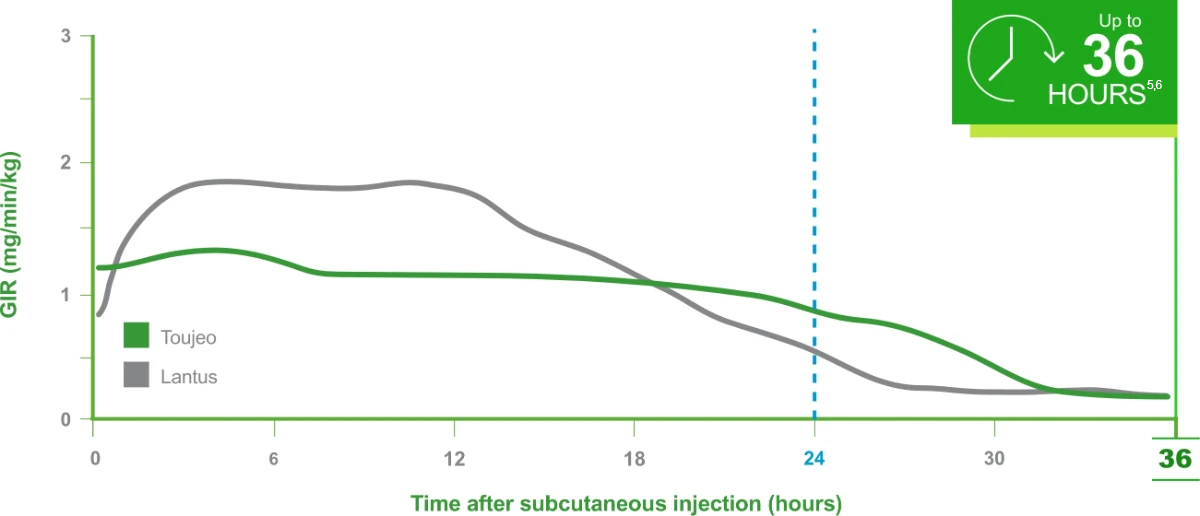
These PK/PD data do not support a comparison of the safety or efficacy of Toujeo and Lantus. 5,6
Clamp Study 1:
The PDs of Toujeo at steady state after 8 days of daily injections were evaluated against Lantus in a euglycemic clamp study of patients with T1DM (N=30) receiving injections of 0.4 U/kg once daily. The dose on Day 8 was followed by a 36-hour euglycemic clamp.
CLAMP Study Limitations: Difficulty in extrapolating results directly to clinical practice due to the experimental clamp setting.5
In pivotal trials, proven A1C reduction and established safety profile in a broad range of adult patients1-4,6
Click on a tab to see efficacy and safety results for each of the EDITION clinical trials.
T2DM: Insulin-naive and previously on OADs1
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T2DM were nasopharyngitis (7.1%) and upper respiratory tract infection (5.7%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 3: A 26-week, open-label, controlled, titrate-to-target, noninferiority study in adults with diabetes not at A1C goal (range: 7% to 10% or 11%) randomized to Toujeo or Lantus once daily. All patients were titrated to an FPG goal of 80-100 mg/dL (T2DM).1-4,6
T1DM: Previously on basal and mealtime insulin2
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T1DM were nasopharyngitis (12.8%) and upper respiratory tract infection (9.5%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 4 was a multicenter, random-ized, four-arm, parallel-group, phase 3a study involving 549 participants with type 1 diabetes who were randomized (1:1:1:1) to once-daily Gla-300 or Gla-100, injected morning or evening, while continuing mealtime insulin.1-4,6
T2DM: Previously on basal and mealtime insulin3
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T2DM were nasopharyngitis (7.1%) and upper respiratory tract infection (5.7%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 1 was a 6-month, multinational, open-label, parallel-group study. Adults with glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) 7.0-10.0% (53-86 mmol/mol) were randomized to Gla-300 or Gla-100 once daily with dose titration seeking fasting plasma glucose 4.4-5.6 mmol/L. Primary end point was HbA1c change from baseline; main secondary end point was percentage of participants with one or more confirmed (≤3.9 mmol/L) or severe nocturnal hypoglycemia from week 9 to month 6.1-4,6
T2DM: Previously on basal insulin and OADs4
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T2DM were nasopharyngitis (7.1%) and upper respiratory tract infection (5.7%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 2 was a multicenter, randomized, open-label, two-arm, parallel-group, phase 3a study 811 participants with type 2 diabetes. The study comprised a 2-week screening phase, followed by a 6-month treatment period and a 6- month safety extension period. The study also included a 4-week post treatment follow-up period to monitor safety and efficacy during the transition back to a commercially available basal insulin.
T2DM: Insulin-naive and previously on OADs1
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T2DM were nasopharyngitis (7.1%) and upper respiratory tract infection (5.7%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 3: A 26-week, open-label, controlled, titrate-to-target, noninferiority study in adults with diabetes not at A1C goal (range: 7% to 10% or 11%) randomized to Toujeo or Lantus once daily. All patients were titrated to an FPG goal of 80-100 mg/dL (T2DM).1-4,6
T1DM: Previously on basal and mealtime insulin2
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T1DM were nasopharyngitis (12.8%) and upper respiratory tract infection (9.5%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 4 was a multicenter, random-ized, four-arm, parallel-group, phase 3a study involving 549 participants with type 1 diabetes who were randomized (1:1:1:1) to once-daily Gla-300 or Gla-100, injected morning or evening, while continuing mealtime insulin.1-4,6
T2DM: Previously on basal and mealtime insulin3
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T2DM were nasopharyngitis (7.1%) and upper respiratory tract infection (5.7%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 1 was a 6-month, multinational, open-label, parallel-group study. Adults with glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) 7.0-10.0% (53-86 mmol/mol) were randomized to Gla-300 or Gla-100 once daily with dose titration seeking fasting plasma glucose 4.4-5.6 mmol/L. Primary end point was HbA1c change from baseline; main secondary end point was percentage of participants with one or more confirmed (≤3.9 mmol/L) or severe nocturnal hypoglycemia from week 9 to month 6.1-4,6
T2DM: Previously on basal insulin and OADs4
Most common adverse events (with incidence ≥5%) with Toujeo in patients with T2DM were nasopharyngitis (7.1%) and upper respiratory tract infection (5.7%).6
- Incidence of severe hypoglycemia when part of a multiple-dose injection regimen: 6.6% in T1DM, 5% in T2DM; when part of a basal insulin-only regimen: 1.0% and 0.9% in two T2DM studies6
- In all the EDITION studies, Toujeo met the primary endpoint (prespecified noninferiority margin of 0.4% and the 95% CI) at 26 weeks6
- In clinical trials, patients on Toujeo used more basal insulin than patients on Lantus (11%-15% in T2DM; 17.5% in T1DM)6
- To minimize the risk of hypoglycemia, titrate the dose of Toujeo no more frequently than every 3 to 4 days6
- Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse event associated with insulin-containing therapies
EDITION 2 was a multicenter, randomized, open-label, two-arm, parallel-group, phase 3a study 811 participants with type 2 diabetes. The study comprised a 2-week screening phase, followed by a 6-month treatment period and a 6- month safety extension period. The study also included a 4-week post treatment follow-up period to monitor safety and efficacy during the transition back to a commercially available basal insulin.
There were no clinically important differences in body weight between treatment groups.6
†Documented symptomatic hypoglycemia <3.0 mmol/L (<54 mg/dL).1
‡Severe hypoglycemia: an event requiring assistance of another person to actively administer a resuscitative action.6
Important Safety Information
A1C, glycated hemoglobin; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; GIR, glucose infusion rate; OAD, oral antidiabetic drug; PD, pharmacodynamics; PK, pharmacokinetics; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
References:
1. Bolli GB, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2015;17(4):386-394. 2. Home PD, et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(12):2217-2225. 3. Riddle MC, et al. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(10):2755-2762. 4. Yki-Järvinen H, et al. Diabetes Care. 2014;37(12):3235-3243. 5. Becker RHA, et al. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(4):637-643. 6. Toujeo Prescribing Information. Sanofi.