OUR MULTI-STEP APPROACH:
Tetanus toxoid was identified as an alternative to the protein carrier used in other US-licensed MenACWY vaccines1-3
Individual conjugate structures were evaluated for each serogroup (A, C, W, and Y)1
Chemical and structural features for each serogroup achieved the demonstrated immune response1
COMMITTED TO THE FIGHT AGAINST MENINGOCOCCAL DISEASE
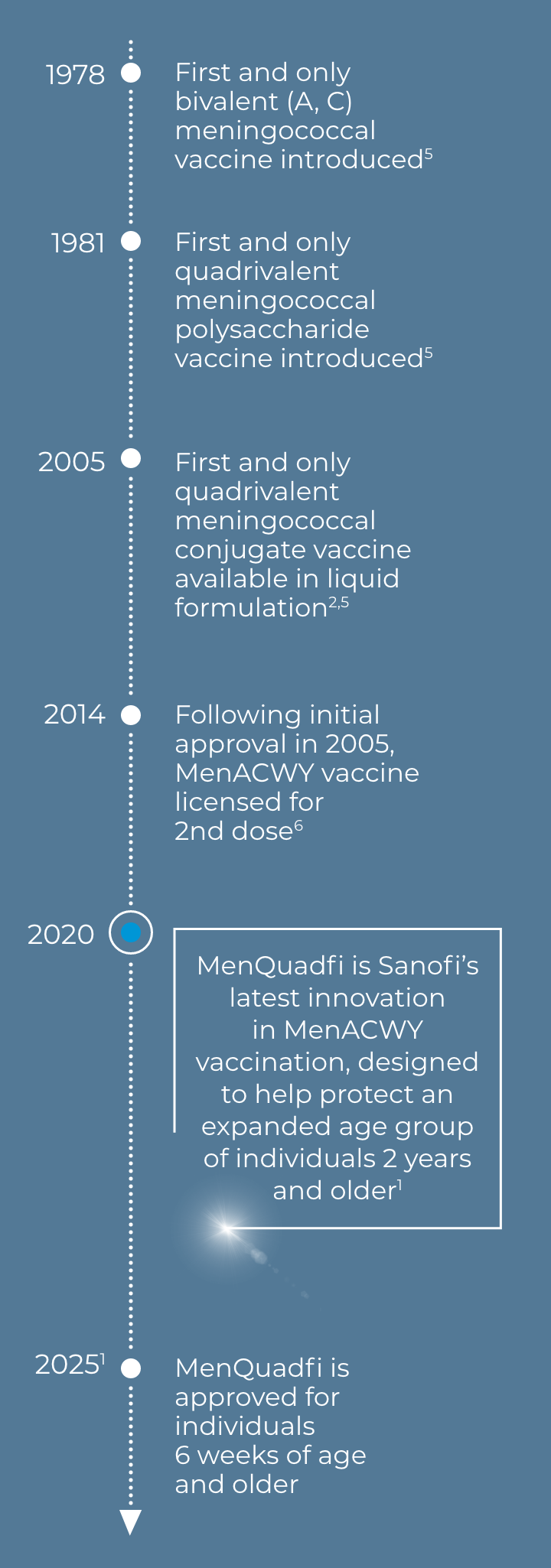
In the US, Sanofi has been a leader in this fight for more than 40 years4
%20(1)%20(6).webp)
SANOFI partners with public health stakeholders to help improve immunization rates and access to vaccines, with a heritage of innovation and partnership that will continue into the future.
Important Safety Information
MenACWY = N meningitidis serogroups A, C, W, and Y.
MenQuadfi is a registered trademark of Sanofi.
REFERENCES:
1. MenQuadfi [Prescribing Information]. Sanofi.
2. Sanofi. Data on File. July 27, 2020.
3. About meningococcal vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Last reviewed November 20, 2023. Accessed June 26, 2025. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/mening/hcp/about-vaccine.html#print
4. Vaccine timeline. Immunization Action Coalition. Updated March 18, 2025. Accessed July 24, 2025. https://www.immunize.org/timeline
5. Menactra [Prescribing Information]. Sanofi.
6. FDA approves use of Menactra® vaccine for booster immunization against potentially deadly disease. Press release. Sanofi; September 8, 2024. Accessed July 30, 2023. https://www.news.sanofi.us/press-releases?item=137127
.webp)
.webp)