Spotlight on AD—the role key cytokines play and a look at the factors that contribute to this condition
Beneath the skin of patients with AD—type 2 inflammation and the cytokines involved.
Deze website is uitsluitend voorbehouden aan beroepsbeoefenaren in Nederland.

Beneath the skin of patients with AD—type 2 inflammation and the cytokines involved.

Tot recent werd gedacht dat COPD, in tegenstelling tot astma, vrijwel niet gekenmerkt wordt door type-2-inflammatie. Inmiddels hebben studies laten zien dat ook bij 30 tot 40% van de patiënten met COPD hiervan sprake is.1-5

COPD wordt traditioneel geassocieerd met een neutrofiel-gedreven ontsteking, maar dat blijkt complexer. Professor of Medicine Surya Bhatt, een gerenommeerd COPD-onderzoeker, laat zien dat eosinofiel-gerelateerde type-2-inflammatie bij een grote groep patiënten voorkomt.

Professor of Medicine Surya Bhatt, een gerenommeerd COPD-onderzoeker, presenteert studiedata die o.a. een verhoogd recidief-risico en verhoogde mortaliteit na een exacerbatie aantonen:

Cytokines die betrokken zijn bij type-2-inflammatie zijn verhoogd tijdens acute exacerbaties en spelen een rol bij de hypersecretie van slijm in de longen. Professor of Medicine Surya Bhatt, een gerenommeerd COPD-onderzoeker, licht dat toe:
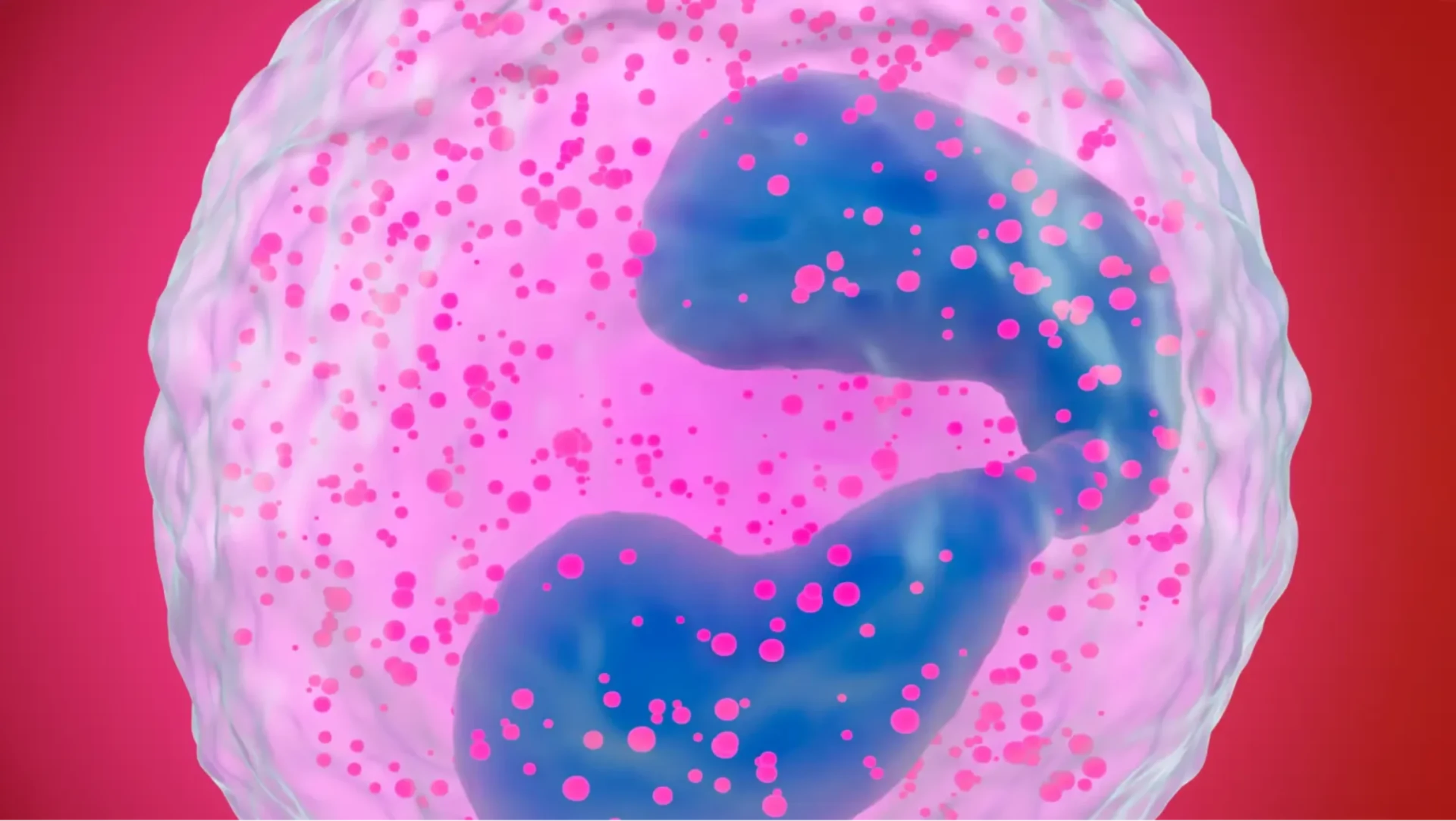
Het aantal eosinofielen in het bloed (BEC) kan fluctueren. Door het eenmalig te bepalen, kun je een hoog BEC missen bij patiënten met fluctuerende eosinofielen.1 Dit is belangrijk, want een hoog BEC heeft een directe relatie met het COPD-exacerbatierisico.1 Alleen door frequent het BEC te meten, identificeer je alle COPD-patiënten met type-2-inflammatie.


Kies één of meerdere presentaties die u graag wilt ontvangen. Wij nemen snel contact met u op om samen een geschikt moment in te plannen.

Wat betekenen de nieuwe aanbevelingen rondom biologics en JAK-remmers voor uw dagelijkse werkwijze?